arp broadcast disable (VLANIF interface view)
Function
The arp broadcast disable command disables a VLANIF interface from broadcasting ARP packets.
The undo arp broadcast disable command enables a VLANIF interface to broadcast ARP packets.
By default, VLANIF interfaces are enabled to broadcast ARP packets.

Only the S5720-EI, S5720-HI, S5730-HI, S5731-H, S5731-S, S5731S-H, S5731S-S, S5732-H, S6720-EI, S6720-HI, S6720S-EI, S6730-H, S6730S-H, S6730-S, and S6730S-S support this command.
Usage Guidelines
Usage Scenario
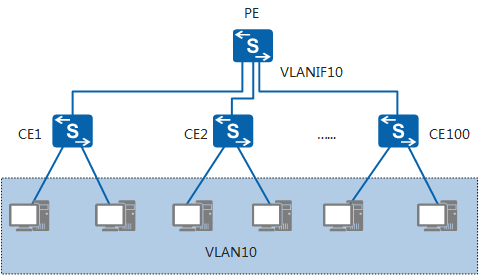
By default, a VLANIF interface broadcasts ARP packets in a VLAN. For example, on the large Layer 2 aggregation network shown in Figure 1, user hosts connect to CE1 through CE100 to access the aggregation device PE that has VLANIF10 configured as the user gateway. As VLANIF10 by default broadcasts ARP packets, these ARP packets are flooded on the user network, consuming a large number of network resources, which affects services and gateway performance.
To ensure user services and aggregation gateway performance, run the arp broadcast disable command to disable the aggregation gateway's VLANIF interface from broadcasting ARP packets.
Precautions
- Proxy ARP scenarios, including intra-VLAN proxy ARP and inter-VLAN proxy ARP
After a VLANIF interface is disabled from broadcasting ARP packets, the proxy does not forward ARP Request messages from a host to their destinations even if all proxy conditions are met. As a result, proxy ARP fails.
- Scenarios in which hosts send unicast packets
For example, in ping operations, ICMP Echo Request messages must be encapsulated with MAC addresses mapped to the destination IP addresses. If the host does not have ARP entries, it must send ARP Request messages to learn the MAC address mapped to the destination IP address. However, the VLANIF interface is disabled from broadcasting ARP packets, and therefore cannot send ARP Request messages. Subsequently, the host cannot obtain the MAC address mapped to the destination IP address, causing a ping operation failure. This problem also occurs in other scenarios in which hosts send unicast packets.
- Strict ARP learning scenarios
In a strict ARP learning scenario, a device learns MAC addresses only of ARP Reply messages in response to ARP Request messages that it sends. If the VLANIF interface is disabled from broadcasting ARP packets, it cannot actively send ARP Request messages. As a result, strict ARP learning fails.
- VLAN aggregation scenarios
If the VLANIF interface is disabled from broadcasting ARP packets, the super VLAN will not broadcast ARP packets to all its sub-VLANs.
After a VLANIF interface is disabled from broadcasting ARP packets, gratuitous ARP packets will still be sent normally.
Switching between enabling and disabling the ARP broadcasting function on a VLANIF interface will cause the direct routes to flap temporarily.