Overview of PPPoE+
Background
PPPoE uses a remote access device to provide the access service for clients on the Ethernet, and controls and charges each connected client. PPPoE uses the client/server model. The PPPoE client sends a connection request to the PPPoE server. After the PPPoE client and PPPoE server complete negotiation, the PPPoE server provides access control and authentication functions.
PPPoE has good authentication and security mechanisms, but has some limitations. The PPPoE server authenticates a user using the user name and password. If the account is embezzled, the embezzler can use the account to access the Internet easily. PPPoE+ is used to solve this problem.
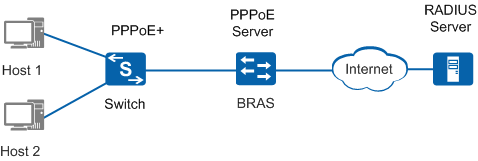
PPPoE+ is deployed on the Switch that is located between PCs and the Broadband Remote Access Server (BRAS), as shown in Figure 1. The Switch sends PPPoE Active Discovery (PAD) packets containing information about the interface connected to the PPPoE client such as the slot ID/subcard ID/interface number, VLAN ID, and MAC address to the PPPoE server. The user account and access interface information are both authenticated by the PPPoE server, preventing user account embezzling.
PPPoE+ working process
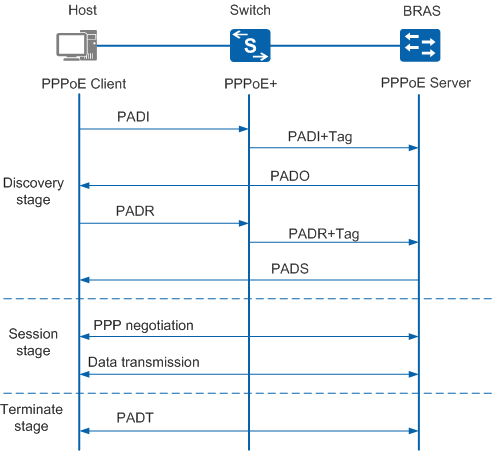
PPPoE involves three stages: Discovery stage, Session stage, and Terminate stage. PPPoE+ is applied in the Discovery stage and Session stage. Figure 2 shows the PPPoE+ working process.
- The PPPoE client sends PPPoE Active Discovery Initial (PADI) packets to the PPPoE server.
- The Switch obtains a PADI packet and adds information about the interface connected to the PPPoE client such as the slot ID/subcard ID/interface number, VLAN ID, and MAC address to the PADI packet in tagged mode, and forwards the packet to the PPPoE server.
- After receiving the PADI packet in tagged mode, the BRAS sends a PPPoE Active Discovery Offer (PADO) packet to the PPPoE client.
- After receiving the PADO packet, the PPPoE client sends a PPPoE Active Discovery Request (PADR) packet.
- After obtaining the PADR packet, the Switch adds PPPoE+ tags to the PADR packet and sends the packet to the BRAS.
- After receiving the PADR packet in tagged mode, the BRAS generates a unique PPP session ID and sends a PPPoE Active Discovery Session-confirmation (PADS) packet to the PPPoE client. If no fault occurs, the BRAS and PPPoE client enter the Session stage.
- At the Session stage, PPP negotiation is performed and PPP packets are transmitted between the PPPoE client and the BRAS. After PPP negotiation is complete, the BRAS encapsulates PPPoE+ tags in the Radius NAS-Port-ID attribute of RADIUS packets and sends the packets to the RADIUS server. The RADIUS server authenticates the user account and access interface information based on the Radius NAS-Port-ID attribute.
- After a PPPoE session is established, the PPPoE client and PPPoE server can send PPPoE Active Discovery Terminate (PADT) packets to end the session.