Overview of RADIUS
AAA can be implemented using multiple protocols. RADIUS is most frequently used in actual scenarios.
RADIUS is a protocol that uses the client/server model in distributed mode and protects a network from unauthorized access. It is often used on networks that require high security and control remote user access. It defines the UDP-based RADIUS packet format and transmission mechanism, and specifies destination UDP ports 1812 and 1813 as the default authentication and accounting ports respectively.
At the very beginning, RADIUS was only the AAA protocol used for dial-up users. As the user access mode diversifies, such as Ethernet access, RADIUS can also be applied to these access modes. RADIUS provides the access service through authentication and authorization and records the network resource usage of users through accounting.
RADIUS has the following characteristics:
Client/Server model
Secure message exchange mechanism
Fine scalability
Client/Server Model
RADIUS client
RADIUS clients run on the NAS to transmit user information to a specified RADIUS server and process requests (for example, permit or reject user access requests) based on the responses from the server. RADIUS clients can locate at any node on a network.
As a RADIUS client, a device supports:
standard RADIUS protocol and its extensions, including RFC 2865 and RFC 2866
Huawei extended RADIUS attributes
RADIUS server status detection
retransmission of Accounting-Request(Stop) packets in the local buffer
active/standby and load balancing functions between RADIUS servers
RADIUS server
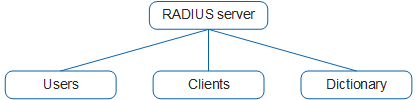
RADIUS servers typically run on central computers and workstations to maintain user authentication and network service access information. The servers receive connection requests from users, authenticate the users, and send all required information (such as permitting or rejecting authentication requests) to the clients. A RADIUS server generally needs to maintain three databases, as shown in Figure 1.
- Users: This database stores user information such as user names, passwords, protocols, and IP addresses.
- Clients: This database stores RADIUS client information, such as the shared keys and IP addresses.
- Dictionary: This database stores the attributes in the RADIUS protocol and their value descriptions.
Secure Message Exchange Mechanism
Authentication messages between a RADIUS server and RADIUS clients are exchanged using a shared key. The shared key is a character string that is transmitted in out-of-band mode, is known to both clients and the server, and does not need to be transmitted independently on the network.
A RADIUS packet has a 16-octet Authenticator field that contains the digital signature data of the whole packet. The signature data is calculated using the MD5 algorithm and shared key. The RADIUS packet receiver needs to verify whether the signature is correct and discards the packet if the signature is incorrect.
This mechanism improves security of message exchange between RADIUS clients and the RADIUS server. In addition, user passwords contained in RADIUS packets are encrypted using shared keys before the packets are transmitted to prevent the user passwords from being stolen during transmission on an insecure network.
Fine Scalability
A RADIUS packet consists of a packet header and a certain number of attributes. The protocol implementation remains unchanged even if new attributes are added to a RADIUS packet.