Disabling ARP Learning for Packets with Double VLAN Tags
Context
If a switch does not need to learn ARP entries from packets with double VLAN tags, you can disable ARP learning for such packets.
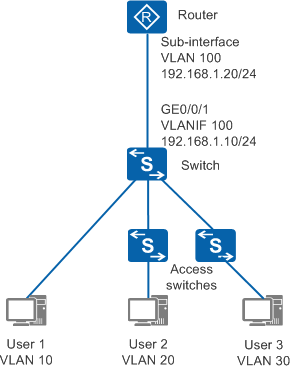
When the router pings the IP address 192.168.1.10 of VLANIF 100 on the switch, the switch learns an ARP entry containing the IP address 192.168.1.20 and VLAN ID 100 of the router's sub-interface.
When the router sends ARP probe packets to a user (for example, user 2) who is not directly connected to the switch, the source IP address in the probe packets is the IP address 192.168.1.20 of the router's sub-interface, and the probe packets contain double VLAN tags. The outer VLAN ID is 100 and the inner VLAN ID is 20. When the probe packets pass through the switch, the switch updates the original ARP entry, and records the outer VLAN ID 100 and inner VLAN ID 20.
By default, the fast ICMP reply function is enabled on the switch. When receiving ICMP request packets, the receiving interface on the switch does not send the packets to the CPU for processing, and instead, directly replies with ICMP reply packets. When the router pings the IP address 192.168.1.10 of VLANIF 100 on the switch, ICMP reply packets match the ARP entry containing the IP address 192.168.1.20, and the ARP entry corresponds to the outer VLAN ID 100 and inner VLAN ID 20. Therefore, ICMP reply packets sent by the switch contain double VLAN tags. When checking the VLAN in received packets, the router detects that the packets contain double VLAN tags instead of one VLAN tag, and discards the packets. Therefore, the router fails to ping the IP address 192.168.1.10 of VLANIF 100 on the switch.
You can disable ARP learning for packets with double VLAN tags on the switch. After this function is disabled, the switch does not learn ARP entries from ARP probe packets with double VLAN tags sent from the router to a user, and does not update the learned ARP entry containing the IP address 192.168.1.20 and VLAN ID 100. The router can always ping the IP address 192.168.1.10 of VLANIF 100 on the switch.

ARP learning for packets with double VLAN tags can be disabled only on the S5720-EI, S5720-HI, S5730-HI, S5731-H, S5731-S, S5731S-S, S5731S-H, S5732-H, S6720-EI, S6720S-EI, S6720-HI, S6730-H, S6730S-H, S6730-S, and S6730S-S.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run interface vlanifvlan-id
A VLANIF interface is created, and the VLANIF interface view is displayed.
- Run arp learning double-tag disable
ARP learning is disabled for packets with double VLAN tags.
By default, ARP learning is enabled on a switch for packets with double VLAN tags.