Example for Configuring DHCP Snooping Attack Defense
Networking Requirements
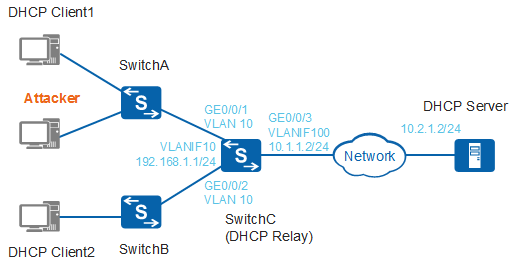
As shown in Figure 1, SwitchA and SwitchB are Layer 2 switches, and SwitchC is the gateway that functions as a DHCP relay agent to forward DHCP messages to the DHCP server, so that DHCP clients can obtain IP addresses and related configurations from the DHCP server.
A network may encounter the following DHCP-based attacks:
- Bogus DHCP server attack: An attacker deploys a DHCP server on the network to allocate IP addresses and network parameters to clients. If the allocated IP addresses and network parameters are incorrect, network services may be interrupted.
- DHCP flood attack: An attacker sends a large number of DHCP messages to a device in a short period of time to generate a huge impact on the device performance. As a result, the device may fail to work.
- Bogus DHCP message attack: An attacker pretends to be an authorized user to continuously send DHCP Request messages to the DHCP server to renew the IP addresses. As a result, the IP addresses cannot be reclaimed and other authorized users cannot obtain IP addresses. If the attacker pretends to be an authorized user to send a DHCP Release message to the DHCP server, the authorized user will be disconnected.
- DHCP server DoS attack: When many attackers apply for IP addresses or an attacker applies for many IP addresses by changing the value of the CHADDR fields in DHCP messages, the IP addresses on the DHCP server are exhausted and authorized users cannot obtain IP addresses.
To prevent DHCP-based attacks and provide high-quality service for DHCP users, configure DHCP snooping attack defense.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Configure the DHCP function so that SwitchC can forward DHCP messages from different network segments to the DHCP server.
- Configure basic functions of DHCP snooping to prevent bogus DHCP server attacks. Enable association between ARP and DHCP snooping to implement real-time binding table update when DHCP users go offline unexpectedly. Configure the device to discard the DHCP messages with non-0 GIADDR fields to prevent attacks initiated by unauthorized users.
- Set the maximum rate of DHCP messages sent to the DHCP message processing unit to prevent DHCP flood attacks. Enable the message discarding alarm. When the number of discarded DHCP messages reaches the maximum value, an alarm is generated.
- Enable the device to check DHCP messages against the binding table to prevent bogus DHCP message attacks. Configure the device to generate an alarm when the number of DHCP messages discarded in binding table checking reaches the threshold.
- Set the maximum number of access users and enable the device to check whether the MAC address in a DHCP Request message header is the same as the CHADDR value in the data field to prevent DHCP server DoS attacks. Configure the device to generate an alarm when the number of messages discarded in CHADDR field check reaches the alarm threshold.
The configurations involved in this example are performed on SwitchC. This example does not provide detailed configurations for the DHCP server.
Procedure
- Configure the DHCP function.
# Configure the DHCP function on the DHCP relay agent.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname SwitchC [SwitchC] dhcp server group dhcpgroup1 [SwitchC-dhcp-server-group-dhcpgroup1] dhcp-server 10.2.1.2 [SwitchC-dhcp-server-group-dhcpgroup1] quit [SwitchC] vlan batch 10 100 [SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type access [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port default vlan 10 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type access [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port default vlan 10 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port link-type access [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port default vlan 100 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit [SwitchC] dhcp enable [SwitchC] interface vlanif 10 [SwitchC-Vlanif10] ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 [SwitchC-Vlanif10] dhcp select relay [SwitchC-Vlanif10] dhcp relay server-select dhcpgroup1 [SwitchC-Vlanif10] quit [SwitchC] interface vlanif 100 [SwitchC-Vlanif100] ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 [SwitchC-Vlanif100] quit [SwitchC] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1
# Assign IP address 10.2.1.2/24 to the DHCP server, configure the address pool 192.168.1.0/24, and set the gateway address of the address pool to 192.168.1.1.
- Enable DHCP snooping.
# Enable DHCP snooping globally and configure the device to process only DHCPv4 messages.
[SwitchC] dhcp snooping enable ipv4# Enable DHCP snooping on the user-side interface. GE0/0/1 is used as an example. The configuration on GE0/0/2 is the same as the configuration on GE0/0/1 and is not mentioned here.
[SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping enable [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Enable association between ARP and DHCP snooping.
[SwitchC] arp dhcp-snooping-detect enable# Enable the device to check whether the GIADDR field in a DHCP Request message is 0. GE0/0/1 is used as an example. The configuration on GE0/0/2 is the same as that on GE0/0/1 and is not mentioned here.
[SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping check dhcp-giaddr enable [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
- Set the maximum rate of DHCP messages sent to the DHCP message processing unit and enable the message discarding alarm.
# Set the maximum rate of sending DHCP messages to the processing unit to 90 pps.
[SwitchC] dhcp snooping check dhcp-rate enable [SwitchC] dhcp snooping check dhcp-rate 90
# Enable the trap function for the rate limit and set the alarm threshold.
[SwitchC] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-rate enable [SwitchC] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-rate threshold 500
- Configure the device to check DHCP messages against the binding table and enable the device to generate an alarm when the number of messages discarded in binding table checking reaches the alarm threshold.
# Configure the user-side interface. GE0/0/1 is used as an example. The configuration on GE0/0/2 is the same as that on GE0/0/1 and is not mentioned here.
[SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping check dhcp-request enable [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request enable [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request threshold 120 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
- Set the maximum number of access users on an interface, enable the device to check whether the MAC address in a DHCP Request message header is the same as the CHADDR value in the data field, and enable the device to generate an alarm when the number of messages discarded in CHADDR field check reaches the alarm threshold.
# Configure the user-side interface. GE0/0/1 is used as an example. The configuration on GE0/0/2 is the same as that on GE0/0/1 and is not mentioned here.
[SwitchC] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping max-user-number 20 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping check dhcp-chaddr enable [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr enable [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr threshold 120 [SwitchC-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display dhcp snooping configuration command to view the DHCP snooping configuration.
[SwitchC] display dhcp snooping configuration # dhcp snooping enable ipv4 dhcp snooping check dhcp-rate enable dhcp snooping check dhcp-rate 90 dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-rate enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-rate threshold 500 arp dhcp-snooping-detect enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 dhcp snooping enable dhcp snooping check dhcp-giaddr enable dhcp snooping check dhcp-request enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request threshold 120 dhcp snooping check dhcp-chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr threshold 120 dhcp snooping max-user-number 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 dhcp snooping enable dhcp snooping check dhcp-giaddr enable dhcp snooping check dhcp-request enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request threshold 120 dhcp snooping check dhcp-chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr threshold 120 dhcp snooping max-user-number 20 #
# Run the display dhcp snooping interface command to view DHCP snooping information on an interface. The values of Check dhcp-giaddr, Check dhcp-chaddr, and Check dhcp-request fields are Enable. Take the display on GE0/0/1 as an example:
[SwitchC] display dhcp snooping interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 DHCP snooping running information for interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 : DHCP snooping : Enable Trusted interface : No Dhcp user max number : 20 Current dhcp and nd user number : 0 Check dhcp-giaddr : Enable Check dhcp-chaddr : Enable Alarm dhcp-chaddr : Enable Alarm dhcp-chaddr threshold : 120 Discarded dhcp packets for check chaddr : 0 Check dhcp-request : Enable Alarm dhcp-request : Enable Alarm dhcp-request threshold : 120 Discarded dhcp packets for check request : 0 Check dhcp-rate : Disable (default) Alarm dhcp-rate : Disable (default) Alarm dhcp-rate threshold : 500 Discarded dhcp packets for rate limit : 0 Alarm dhcp-reply : Disable (default)
Configuration Files
SwitchC configuration file
# sysname SwitchC # vlan batch 10 100 # dhcp enable # dhcp snooping enable ipv4 dhcp snooping check dhcp-rate enable dhcp snooping check dhcp-rate 90 dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-rate enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-rate threshold 500 arp dhcp-snooping-detect enable # dhcp server group dhcpgroup1 dhcp-server 10.2.1.2 0 # interface Vlanif10 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 dhcp select relay dhcp relay server-select dhcpgroup1 # interface Vlanif100 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type access port default vlan 10 dhcp snooping enable dhcp snooping check dhcp-giaddr enable dhcp snooping check dhcp-request enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request threshold 120 dhcp snooping check dhcp-chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr threshold 120 dhcp snooping max-user-number 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type access port default vlan 10 dhcp snooping enable dhcp snooping check dhcp-giaddr enable dhcp snooping check dhcp-request enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-request threshold 120 dhcp snooping check dhcp-chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr enable dhcp snooping alarm dhcp-chaddr threshold 120 dhcp snooping max-user-number 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type access port default vlan 100 # ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.1.1 # return