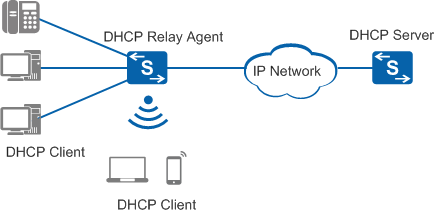
Network Elements in DHCP
A client-server model forms the basis of DHCP and consists of two roles that a Huawei switch can fulfill: DHCP server and DHCP client. When the DHCP server and client are on different network segments, there is a DHCP relay agent between them. Figure 1 shows the typical DHCP networking.
The following describes the three roles involved in DHCP:
DHCP server
A DHCP server assigns IP addresses from specified address pools to DHCP clients. It can also manage these clients and provide network parameters such as the default gateway address, Domain Name System (DNS) server address, and Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) server address. A DHCP server can accept broadcasts from locally attached LAN segments or DHCP requests forwarded by DHCP relay agents within the network.
DHCP client
A client can use BOOTP or DHCP to obtain its IP address and other network parameters from a DHCP server. To obtain an IP address, the client sends a BOOTP or DHCP Request message. DHCP clients can be IP phones, PCs, mobile devices, diskless workstations, or other networked devices, and can be connected directly or through other networks using DHCP relay agents.
DHCP relay agent
DHCP relay agent forwards DHCP messages between a DHCP server and DHCP clients and helps the DHCP server to dynamically allocate network parameters to the DHCP clients.
When a DHCP client broadcasts DHCP Discovery messages with the destination IP address 255.255.255.255, only the DHCP server on the same network segment as the DHCP client can receive the messages. If a DHCP server is on a different network segment from the DHCP client, a DHCP relay agent must be deployed to forward DHCP Discovery messages to the DHCP server. The DHCP relay agent modifies the format of a DHCP Discovery or Offer message to generate a new DHCP message and then forwards it.