Interface Numbering Rules
Management Interface Numbering Rules
The following table lists the management interface numbers.
Interface |
Number |
|---|---|
Console interface |
console 0 |
MEth interface |
MEth 0/0/1 NOTE:
Only S5720-50X-EI-46S-AC, S5720-50X-EI-46S-DC, S5720-50X-EI-AC, S5720-50X-EI-DC, S5720-EI, S5720-HI, S5720S-SI, S5720-SI, S5735-S, S5735S-S, S5735-S-I, S5730-HI, S5730S-EI, S5730-SI, S5731-H, S5731-S, S5731S-H, S5731S-S, S5732-H, S6720-EI, S6720-HI, S6720-LI, S6720S-EI, S6720S-LI, S6720S-SI, S6720-SI, S6730-H, S6730S-H, S6730-S, and S6730S-S support MEth management interface. The S5720-50X-EI-46S-AC, S5720-50X-EI-46S-DC, S5720-50X-EI-AC, S5720-50X-EI-DC, or S5720I-SI switch automatically generates a virtual interface MEth 0/0/1. On a standalone switch, the configuration of this interface does not take effect. In a stack, if there are stack members that support management interfaces, the configuration of MEth 0/0/1 takes effect. If there is no stack member that supports management interfaces, the configuration of MEth 0/0/1 interface still does not take effect. |
Physical Interface Numbering Rules
Physical interfaces are numbered in the following way:
- Slot ID: indicates the slot where the switch is located. The value is 0.
- Subcard ID: indicates the ID of a subcard.
- Interface sequence number: indicates the sequence number of an interface on the switch.
- Stack ID: indicates the ID of a stacked switch. The value ranges from 0 to 8.
- Subcard ID: indicates the ID of a subcard.
- Interface sequence number: indicates the sequence number of an interface on the switch.
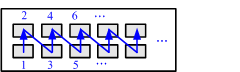
As shown in Figure 1, There are two rows of service interfaces on the device. These interfaces are numbered from bottom to top and left to right, starting from 1.
For example, the interface on the top left is numbered 0/0/2.
10GE interfaces converted from a 40GE interface are numbered based on the number of the last 10GE interface on the switch. For interfaces on the switch panel, if the last 10GE interface is numbered XGE 0/y/m and a 40GE interface to be split is numbered 40GE 0/y/n, the four 10GE interfaces converted from the 40GE interface are numbered XGE 0/y/(m + 4 * (n - 1) + 1). For example, if the last 10GE interface on a switch is numbered XGE 0/0/48, the four 10GE interfaces converted from 40GE 0/0/3 are numbered XGE 0/0/57, XGE 0/0/58, XGE 0/0/59, and XGE 0/0/60. For interfaces on a card, m has a fixed value of 0. For example, the four 10GE interfaces converted from 40GE 1/1/1 on a card are numbered XGE 1/1/1, XGE 1/1/2, XGE 1/1/3, and XGE 1/1/4.
- y: indicates the subcard number.
- m: indicates the sequence number of the last 10GE interface on the switch.
- n: indicates the sequence number of the 40GE interface.

Split interfaces are numbered in the same sequence as the wires of a cable are numbered. For example, in a 1-to-4 cable, the wire numbered 1 corresponds to the interface with the lowest interface number, and the wire numbered 4 corresponds to the interface with the highest interface number.