Configuring Virtual Cable Test
Context
Virtual cable test (VCT) technology uses time domain reflectometry (TDR) to detect the cable status. When pulse signals are transmitted in a cable, some energy of the signals is reflected at the end or a failure point on the cable. This phenomenon is called TDR. The VCT algorithm measures the time spent on transmitting pulse signals over a cable, reaching the failure point, and returning the pulse signals. The measured time is converted into the distance.
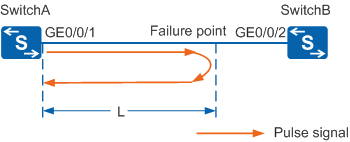
As shown in Figure 1, GE0/0/1 of SwitchA is connected to GE0/0/2 of SwitchB using a network cable. A failure point exists on the network cable. After VCT is configured on GE0/0/1, the system generates pulse signals. When the pulse signals reach the failure point, some energy is reflected to the GE0/0/1. In this example, the distance between SwitchA and the failure point is L, the period from sending pulse signals to receiving reflected pulse signals is T, and the transmission rate of pulse signals in the cable is V. The following formula is used to calculate the distance between the failure point and GE0/0/1:
L = (V x T)/2
VCT detects the network cable fault type and identifies the failure point, facilitating fault location on network cables.

The following devices do not support this function:
- Multi-GE interfaces on the S5720-28X-PWH-LI-AC, S5732-H24UM2CC, S5732-H48UM2CC, S6720-32C-SI-AC, S6720-32C-SI-DC, S6720-32C-PWH-SI-AC, S6720-32C-PWH-SI, S6720-52X-PWH-SI, S6720-56C-PWH-SI-AC, and S6720-56C-PWH-SI
- XGE electrical interfaces on the ES5D21X08T00 card
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run interface interface-type interface-number
The interface view is displayed.
- Run virtual-cable-test
VCT is configured.

- The test result is only for reference and may be inaccurate for cables of some vendors.
- If the detection result is Unknown, you are advised to use the cable analyzer to perform the test.
- The test result is related to the cable signal attenuation. When the cable length is shorter than 3 m, the cable signal attenuation mostly results from the connector, not the cable. The test result is therefore invalid.
- Running the virtual-cable-test command may affect services on the interface in a short period of time, and the interface in Up state may alternate between Up and Down.
- Combo electrical interfaces support cable tests, but cable tests are not recommended on combo electrical interfaces because services will be interrupted.
- This command can be used on an XGE optical interface or GE optical interface when the interface has a GE copper module installed.
- After a 25GE optical interface is configured to work at the rate of 1 Gbit/s using the port mode ge command and has a GE copper module installed, the virtual-cable-test command can be configured on the interface.
- On the S2720-EI, S5720-LI, S5735-L, S5735S-L, S5735S-L-M, S5720S-LI, S5730-SI, S5730S-EI, S6720-LI, S6720-SI, S6720S-SI, S6720S-LI, S5720-SI, S5735-S, S5735S-S, S5735-S-I, S5720I-SI, and S5720S-SI, when a GE electrical interface works at a rate of 1000 Mbit/s or 100 Mbit/s, the test result is only for reference and may be inaccurate if the interface is in Up state.
- On the S5720-EI, S5720-HI, S5730-HI, S6720-HI, S6720S-EI, S5732-H, S6730-H, S6730S-H, S6730-S, S6730S-S, and S6720-EI, when a GE electrical interfaceworks at a rate of 100 Mbit/s, the test result is only for reference and may be inaccurate.
- On the S5731-H, S5731S-H, S5731-S, and S5731S-S, when a GE electrical interface works at a rate of 10 Mbit/s, 100 Mbit/s, or 1000 Mbit/s, the test result is only for reference and may be inaccurate.
- The test result is only for reference and may be inaccurate when the interface is in the Up state or the remote interface is shut down.
- The FE electrical port uses only two pairs of wire pairs. The two pairs of wire sequences used for VCT detection are unavailable.
- When the GE electrical port works at the rate of 10 Mbit/s or 100 Mbit/s, only two pairs of cables are used to detect the VCT status. The other two pairs of cables do not detect and return the default result.
- The virtual cable test (VCT) cannot be performed on multiple interfaces of the device at the same time.