Configuring Route Exchange Between PE device and CE Devices
Context
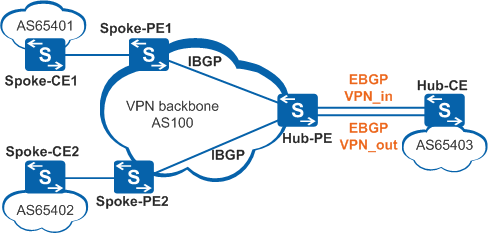
The Hub-PE and Hub-CE devices can use IGP or EBGP to exchange routing information. When they use EBGP, you must configure the Hub-PE device to allow repeated local AS number.
Procedure
- Configure EBGP between the Hub-PE and Hub-CE devices.
For detailed configuration procedures, see Configuring a Routing Protocol Between PE device and CE.
The Spoke-PE and Spoke-CE devices can use EBGP, IGP, or static routes.
To set up an EBGP peer relationship between the Hub-PE and Hub-CE devices and between a Spoke-PE device and a Spoke-CE device, perform the following steps on the Hub-PE device:
- Configure an IGP between the Hub-PE and Hub-CE devices.
For detailed configuration procedures, see Configuring a Routing Protocol Between PE and CE.
Only IGP or static routes can be used between the Spoke-PE and Spoke-CE devices. BGP can cause route flapping between them. If BGP is used, the source BGP route's AS number will get lost when the route is transmitted through the IGP running between the Hub-PE and Hub-CE. The Spoke-PE will receive both the source BGP route sent by the Spoke-CE and the source BGP route with no AS number forwarded by the Hub-PE. The source BGP route sent by the Spoke-CE has an AS number and is therefore not preferred by the Spoke-PE. After the route is withdrawn, the Spoke-PE prefers the source BGP route received from the Spoke-CE again and advertises this route again. As this process repeats, route flapping occurs.
- Configure static routes between the Hub-PE and the Hub-CE
devices.
For detailed configuration procedures, see Configuring a Routing Protocol Between PE device and CE.
EBGP, IGP, or static routes can be used between the Spoke-PE and the Spoke-CE devices.
If the Hub-CE device uses the default route to access the Hub-PE device, perform the following steps on the Hub-PE device to advertise the default route to all the Spoke-PE devices: