MAC Address Flapping
What Is MAC Address Flapping
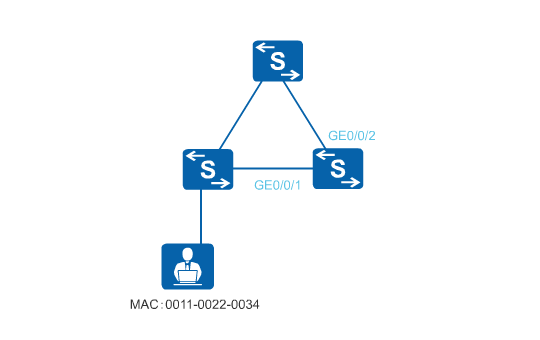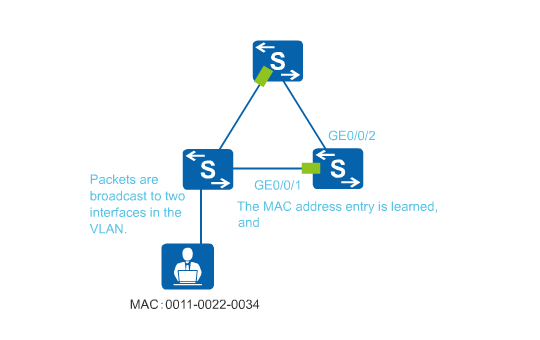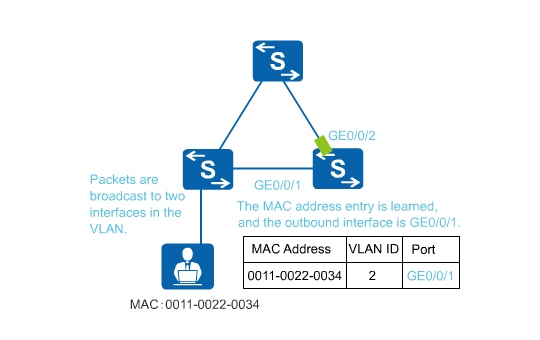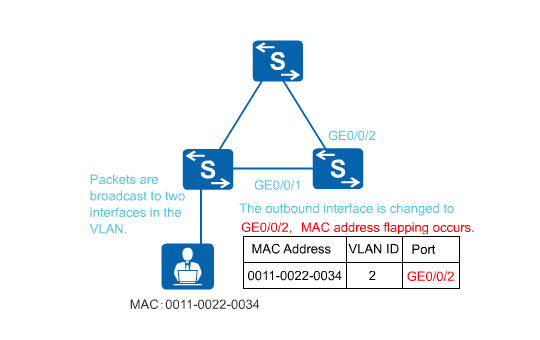
MAC address flapping occurs when a MAC address is learned by two interfaces in the same VLAN and the MAC address entry learned later overrides the earlier one. Figure 1 shows how MAC address flapping occurs. In the MAC address entry with MAC address 0011-0022-0034 and VLAN 2, the outbound interface is changed from GE0/0/1 to GE0/0/2. MAC address flapping can cause an increase in the CPU usage on the switch.
Generally, MAC address flapping does not occur unless a network loop occurs. If frequent MAC address flapping occurs on your network, alarms and MAC address flapping records provide insight for locating faults and eliminating loops.
How to Detect MAC Address Flapping
MAC address flapping detection checks whether outbound interfaces in MAC address entries change frequently.
After MAC address flapping detection is enabled, the switch reports an alarm if MAC address flapping occurs (for example, due to a loop between the outbound interfaces). The alarm contains the flapping MAC address, VLAN ID, and outbound interfaces between which the MAC address flaps. The network administrator can locate the cause of the loop based on the alarm. As an alternative, the switch can perform the action specified in the configuration of MAC address flapping detection to remove the loop automatically. The action can be quit-vlan (remove the interface from the VLAN) or error-down (shut down the interface).
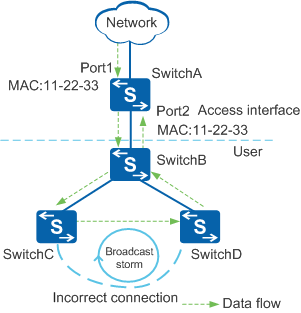
In Figure 2, a network cable is incorrectly connected between SwitchC and SwitchD, causing a loop between SwitchB, SwitchC, and SwitchD. When Port1 of SwitchA receives a broadcast packet, SwitchA forwards the packet to SwitchB. The packet is then sent to Port2 of SwitchA. After being configured with MAC address flapping detection, SwitchA can detect that the source MAC address of the packet flaps from Port1 to Port2. If the MAC address flaps between Port1 and Port2 frequently, SwitchA reports an alarm.

MAC address flapping detection allows a switch to detect changes in traffic transmission paths based on learned MAC addresses. However, the switch cannot obtain the entire network topology. It is recommended that this function be used on an interface connected to a user network where loops may occur.
How to Prevent MAC Address Flapping
MAC address flapping occurs on a network when loops or attacks occur.
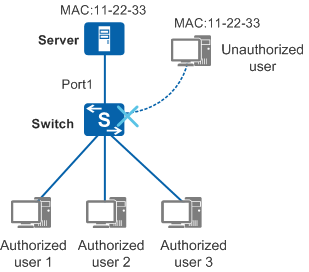
- Increase the MAC address learning priority of an interface: If the same MAC address is learned on interfaces that have different priorities, the MAC address entry on the interface with the highest priority overrides that on the other interfaces.
- Prevent MAC address entries from being overridden on interfaces with the same priority: If the interface connected to a bogus network device has the same priority as the interface connected to an authorized device, the MAC address entry of the bogus device learned later does not override the original correct MAC address entry. If the authorized device is powered off, the MAC address entry of the bogus device is learned. After the authorized device is powered on again, its MAC address cannot be learned.