Traffic Mirroring
Implementation
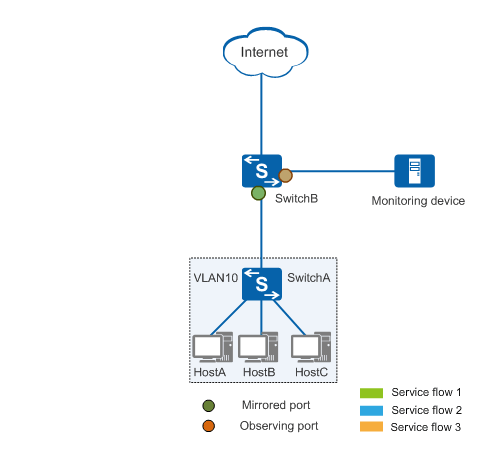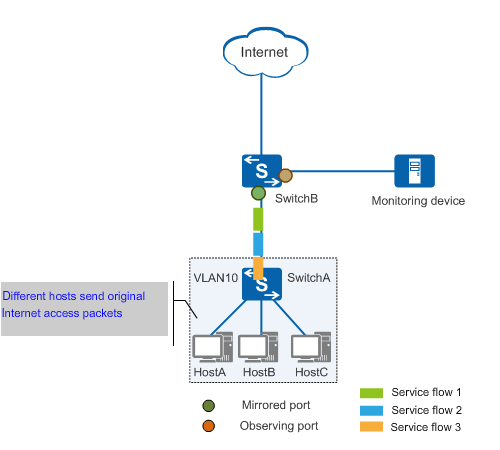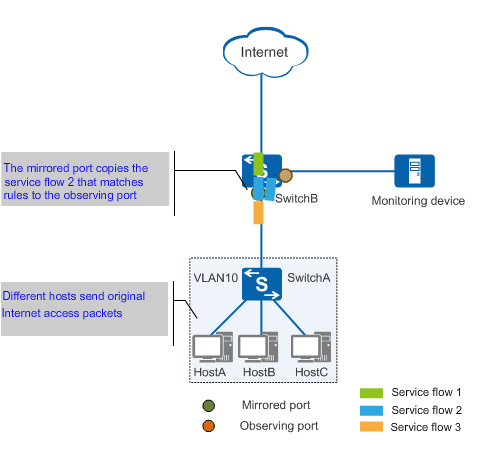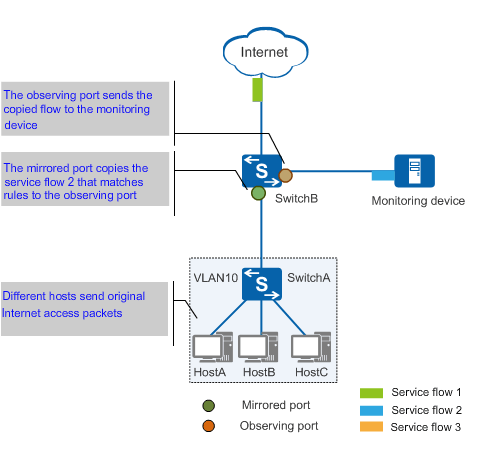
Traffic mirroring copies traffic matching specified rules from one or more mirrored ports to one or more observing ports, which then send the traffic to monitoring devices for analysis. Figure 1 shows the process of traffic mirroring. The mirrored port copies service flow 2 that matches rules to the observing port, which then forwards the copied flow to the monitoring device.
Similar to port mirroring, traffic mirroring is classified into local traffic mirroring and Layer 2 remote traffic mirroring depending on the observing port type.
Traffic Mirroring Rules
- Using MQC: It is complex to configure but supports more matching rules than ACL. MQC-based traffic mirroring can be applied to both inbound and outbound directions.
- Using ACL: It is easy to configure but supports fewer matching rules than MQC. ACL-based traffic mirroring can only be applied to the inbound direction.
For details about traffic policies, see MQC Configuration and ACL-based Simplified Traffic Policy Configuration in the S2720, S5700, and S6700 V200R019C10 Configuration Guide - QoS.
In Layer 2 remote traffic mirroring, if a traffic policy containing traffic mirroring is applied in a VLAN, the VLAN cannot be the Layer 2 remote mirroring VLAN used on the intermediate Layer 2 network to forward mirrored packets.