Configuration Procedure for NAC
Pre-configuration Tasks
NAC only provides multiple network access control protocols for users. To completely authenticate user identity and control users' network access rights, complete the following AAA configuration tasks before configuring NAC:
- Configure the domain and AAA scheme.
- Configure the user name and password on the RADIUS or HWTACACS server if RADIUS or HWTACACS authentication is used.
- Configure the user name and password on the network access device if local authentication is used.
For details about how to configure the AAA client, see AAA Configuration.
Configuration Procedure
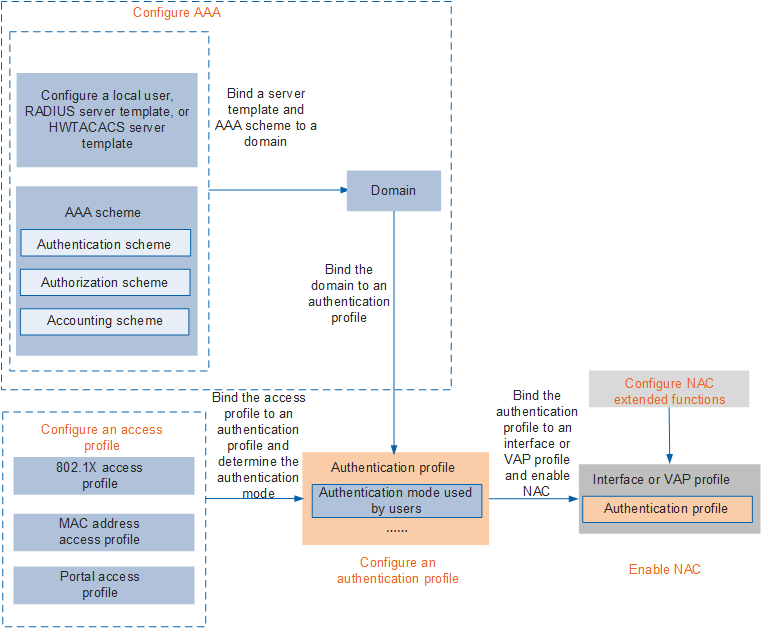
NAC Configuration Tasks
Authentication Mode |
Scenario |
Task |
|---|---|---|
802.1X authentication |
Users are densely distributed and high information security is required. |
Perform the following configurations in sequence:
|
MAC Address authentication |
Dumb terminals such as printers and fax machines need to connect to the network. |
Perform the following configurations in sequence:
|
Portal authentication |
Users are sparsely distributed and move frequently. Portal servers are classified into built-in and external Portal servers. A built-in Portal server is integrated in an access device, whereas an external Portal server has independent hardware. Compared with the external Portal server, the built-in Portal server supports more flexible deployment, but provides only basic functions of the external Portal server. |
When using an external Portal server for authentication, perform the following configurations in sequence:
When using a built-in Portal server for authentication, perform the following configurations in sequence:
|
Multi-mode authentication |
The device allows multiple authentication modes to be deployed simultaneously to meet various authentication requirements on the network. To configure multi-mode authentication of several authentication modes, you only need to bind corresponding access profiles to an authentication profile. The device triggers the corresponding authentication based on received authentication packets. |
Perform the following configurations in sequence:
|