802.1X Timers
802.1X relies on several timers to control the number of packet retransmission times and timeout interval. This section outlines the timers on the device that are relevant to the 802.1X authentication process.
Timeout Timers for EAP-Request/Identity Packets
This section discusses the timers that control the timeout and retry behavior of an 802.1X-enabled interface for sending EAP-Request/Identity packets.
During 802.1X authentication, the device sends an EAP-Request/Identity packet for the user name. The device waits for a period of time defined by a timer, and then sends another EAP-Request/Identity packet if no response is received. The number of times it resends the EAP-Request/Identity packets is defined by the dot1x retry max-retry-value variable.
Figure 1 shows the operation of the timer when MAC address bypass authentication is not configured. If EAP-Request/Identity packets time out, the device sends an EAP failure packet to the client and starts a failover mechanism (Portal authentication or granting specified access permissions) if configured. In this situation, the timer is defined by the dot1x timer tx-period tx-period command. The total time it takes for 802.1X to time out is determined by the following formula:
Timeout = (max-retry-value +1) x tx-period-value
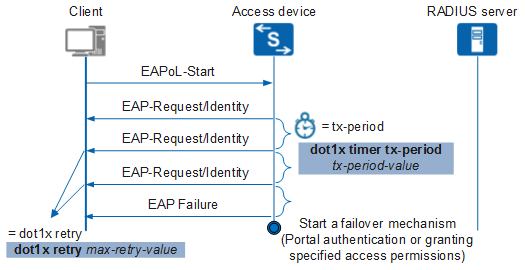
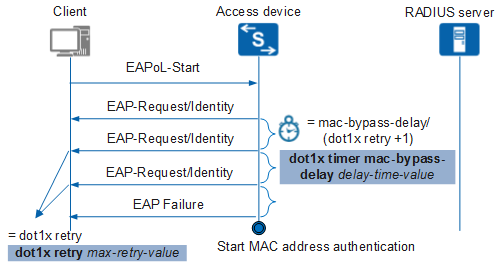
Figure 2 shows the operation of the timer when MAC address bypass authentication is configured. The device performs 802.1X authentication first and starts the timer defined by the dot1x timer mac-bypass-delay delay-time-value command. If 802.1X authentication is not successful before the timer expires, the device performs MAC address authentication for terminals. In this situation, the interval at which the device resends an EAP-Request/Identity packet is the integer of the result calculated as follows: delay-time-value/(max-retry-value+1).
Timeout Timers for EAP-Request/MD5 Challenge Packets
This section discusses the timers that control the timeout and retry behavior of an 802.1X-enabled interface for sending EAP-Request/MD5 Challenge packets.
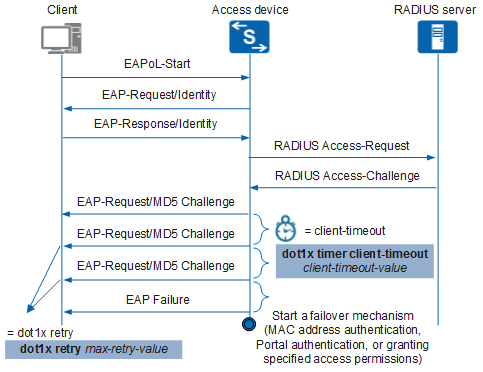
During 802.1X authentication, the device sends an EAP-Request/MD5 Challenge packet to request the client's password in ciphertext. It waits for a period of time defined by the client timeout timer, and then sends another EAP-Request/MD5 Challenge packet. The number of times it resends the EAP-Request/MD5 Challenge packets is defined by the dot1x retry max-retry-value variable. This prevents repeated retransmission of authentication requests, which occupies lots of resources.
As shown in Figure 3, EAP-Request/MD5 Challenge packets time out, and then the device sends an EAP Failure packet to the client and starts a failover mechanism (MAC address authentication, Portal authentication, or granting specified access permissions) if configured. The total time it takes for EAP-Request/MD5 Challenge packets to time out is determined by the following formula:
Timeout = (max-retry-value + 1) x client-timeout-value
Quiet Timer
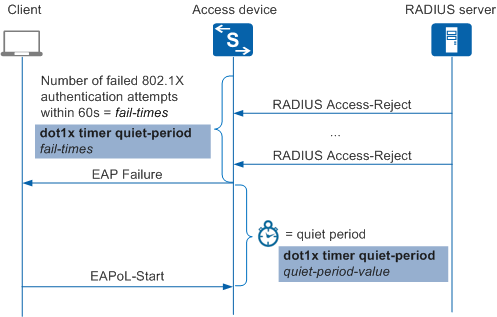
This section discusses the timer that controls when 802.1X restarts after the number of failed 802.1X authentication attempts within 60 seconds reaches the value specified by the dot1x quiet-times fail-times command.
If 802.1X fails and there are no failover mechanisms enabled, the device waits for a period of time known as the quiet-period (configured by the dot1x timer quiet-period quiet-period-value command). During this period of time, the device discards users' 802.1X authentication request packets, avoiding frequent authentication failures.