MAC Address Bypass Authentication
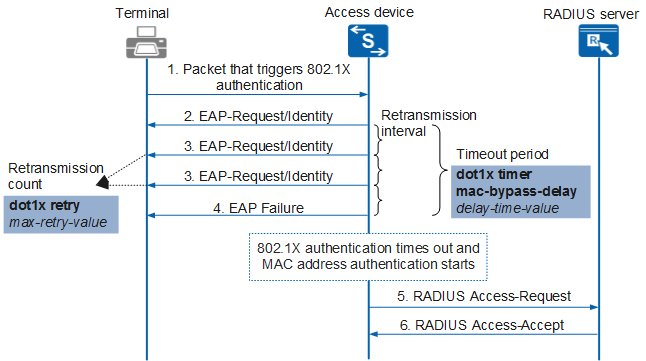
The combination of 802.1X authentication and its fallback mechanism MAC address authentication is called MAC address bypass authentication. With this feature, dumb terminals such as printers and fax machines can connect to the network through MAC address authentication. Figure 1 shows the MAC address bypass authentication process.
Authentication Process
- When an interface of the access device where MAC address bypass authentication is enabled receives a packet from the terminal, 802.1X authentication is first performed for the terminal.
- The access device sends an EAP-Request/Identity packet to request the user's client program to send the entered user name.
- If the access device does not receive any response packet within the retransmission interval, it resends EAP-Request/Identity packets until the configured retransmission count is reached.
- If all requests go unanswered, the access device sends an EAP Failure packet to the terminal.
- In this case, 802.1X authentication times out. The access device sends the user name and password to the RADIUS server for MAC address authentication.
- The RADIUS server compares the received user name and password with the locally saved user name and password. If they are the same, MAC address authentication succeeds and the RADIUS server sends a RADIUS Access-Accept packet to the device.