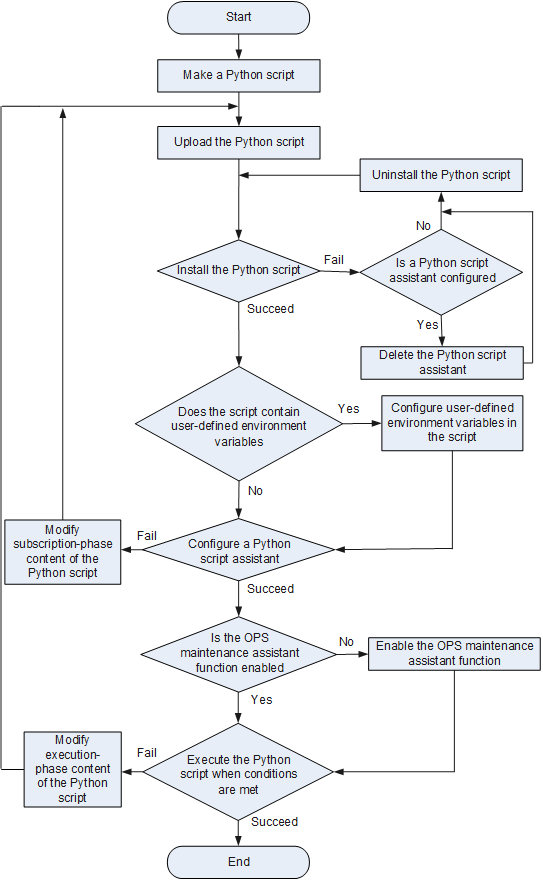
OPS Operation Process
Figure 1 shows the OPS operation process.
The OPS operation process includes the following steps:
- Users make a Python script file locally and use OPS APIs to define
functions.

When making a Python script file, you can use environment variables. For detailed environment variable descriptions, see Environment Variable.
- Upload the Python script to the device.
- Install the Python script. If an installed Python script needs to be modified, uninstall it first, and reinstall it after modification. To uninstall the script for which a script assistant has been configured, delete the assistant first.
- If user-defined environment variables are used in the Python script, configure values of the user-defined environment variables.
- Configure a Python script assistant to register the subscription event in the Python script. When the specified trigger condition is met, the device automatically executes the actions defined in the script. If the subscribed contents in the Python script are incorrect, the device displays an error message to indicate the error location. You need to correct the subscribed contents, upload the script again, and then install the script.
- Enable the OPS maintenance assistant function. After the Python
script assistant is configured, the OPS maintenance assistant function
is enabled by default. If the OPS maintenance assistant function is
disabled, you need to manually enable this function.

The Python script assistance takes effect for a single Python script. Configuring the Python script assistant helps the completion of subscription event registration in the Python script.
The OPS maintenance assistant function takes effect for all Python script assistants. If the OPS maintenance assistant function is disabled, all Python script assistants are not executed.
- After a script assistant is configured and the subscription event is registered successfully, the device executes the actions defined in the Python script successfully when the trigger condition is met, as long as the Python script is correct. If the script is incorrect, the device cannot execute the actions, requiring you to correct the script and then upload and install the script again.
- The device successfully runs the Python script to implement the user-defined functions.
Environment Variable
When subscribing to an event or defining the execution action in a Python script, you can use environment variables. Event subscription is performed in the subscription phase and action execution is performed in the execution phase.
An environment variable consists of a name and a value. Currently, OPS supports system and user-defined environment variables.
System environment variables
Environment variables supported by the device by default cannot be created, deleted, or modified. A system environment variable name starts with a _, and a system environment variable value is determined by the system.
System environment variables include:
Public environment variables: can be used for all types of events.
Non-public environment variables: can only be used for specified events. Its value is obtained when an event is triggered and indicates some information about the event.
For system environment variables currently supported by the OPS, see Table 1 in Obtaining Environment Variable.
For example, you can subscribe to a command entered on a device using the Command Line Event Subscription API. When the subscribed event is matched and you want to know about view information about the command, use the system environment variable _cli_view.value, loginfo = ops.environment.get("_cli_view")User-defined environment variables
In a Python script, you can input an environment variable name in the location where a parameter needs to be input to indicate that an environment variable value needs to be referenced. When the system is running a Python script, it replaces an environment variable name with an environment variable value. To change the value, you can directly change it on the device without having to change and install the Python script. You can define and use user-defined environment variables to simplify the configuration and improve flexibility and feasibility of the Python script.
User-define environment variables start with letters, can contain letters, digits, and _, apply to all types of events, and can be used in subscription and execution phases. The value of a user-defined environment variable can be configured using the environment command. You can create, modify, and delete user-defined variables.
For example, a user wants to subscribe to changes of OSPF routes on the network segment 10.2.1.0/24 in the Python script, and then needs to subscribe to changes of OSPF routes on the network segment 10.2.2.0/24. To omit the process of uninstalling the original script and installing a new script, you can define an environment variable in the subscription phase, and specify the value of the environment variable using the environment command.
value, descri_str = ops.route.subscribe("route1", "ospf_routes", 24, minLen=None, maxLen=None, neLen=None, optype="all", protocol="ospf") # ospf_routes is a user-defined environment variable