Configuring Equal-Cost Routes
Context
If the destinations and costs of multiple routes discovered by one routing protocol are the same, these routes are equal-cost routes and load balancing can be implemented among them.
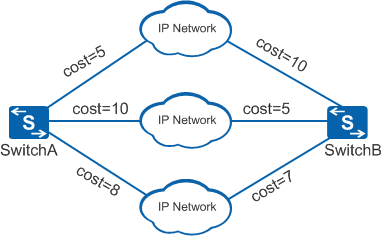
For example, in Figure 1, three routes between switchA and switchB that run OSPF have the same costs. The three routes are equal-cost routes for load balancing.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run ospf [ process-id ]
The OSPF process view is displayed.
- Run maximum load-balancing number
The maximum number of equal-cost routes is set.
By default, the maximum number of equal-cost routes on the S5720I-SI, S5720S-SI, S5720-SI, S5735-S, S5735S-S, S5735-S-I, S5730S-EI, S5730-SI, S6720S-SI, or S6720-SI is 8, and the maximum number of equal-cost routes on the S5720-EI, S5720-HI, S5730-HI, S5731-H, S5731-S, S5731S-H, S5731S-S, S5732-H, S6720-EI, S6720-HI, S6720S-EI, S6730-H, S6730S-H, S6730-S, or S6730S-S is 16.
- (Optional) Run nexthop ip-address weight value
The route preferences are configured for load balancing.
When the number of equal-cost routes on the live network exceeds the limit specified in the maximum load-balancing command, valid routes are randomly selected for load balancing. To specify valid routes for load balancing, you can run the nexthop command to set the route preferences of the routes to higher values.
A smaller value of weight indicates a higher route preference. The default value of weight is 255, which indicates that load balancing is implemented regardless of the route preferences.