Overview of DHCP Policy VLANs
Background
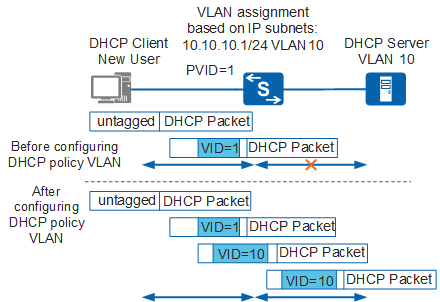
On a network supporting VLAN assignment based on IP subnets, the DHCP policy VLAN allows communication between hosts that access the network for the first time and the DHCP server. The hosts can obtain valid IP addresses and network settings from the DHCP server. Upon receiving an untagged packet from a host, a switch adds a VLAN ID to the packet based on the source IP address of the packet. The host does not have a valid IP address and uses the IP address 0.0.0.0 for temporary communication. The DHCP packet with the source IP address 0.0.0.0 cannot be added to any VLAN based on IP subnets. The switch adds the default VLAN ID of the interface receiving the packet to the packet. Generally, the interface VLAN ID is different from the VLAN to which the DHCP belongs. Therefore, the DHCP server does not allocate the IP address or network settings to the host.
As shown in Figure 1, after the DHCP policy VLAN is configured, the switch sets the VLAN ID of the packet to the same as that of the DHCP server. In this way, the host can communicate with the DHCP server using DHCP packets. After the host obtains a valid IP address and network settings, packets from the host are added to the VLAN assigned based on IP subnets.
You can configure three types of DHCP policy VLAN on the device. They are listed in descending order based on priorities as follows: MAC address-based, interface-based, and generic DHCP policy VLANs.
The DHCP policy VLAN allows for setting 802.1p priorities of DHCP packets so that DHCP traffic is controlled and scheduled by quality of service (QoS).