Application Scenarios for Congestion Avoidance and Congestion Management
Congestion Avoidance
When congestion occurs or worsens, congestion avoidance discards low-priority packets to relieve network overload and ensure forwarding of high-priority packets.
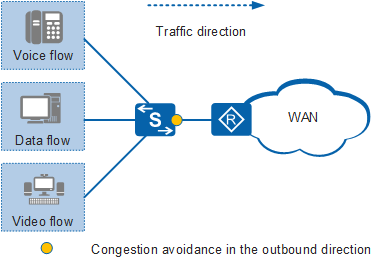
In Figure 1, users on different LANs may obtain data from the same server. Data exchanged between the server and users goes through the wide area network (WAN).
The WAN bandwidth is lower than the LAN bandwidth, so congestion may occur between the WAN and LAN.
Congestion avoidance can be configured to discard low-priority packets, such as data packets. This mitigates network congestion and ensures forwarding of high-priority services.
Congestion Management
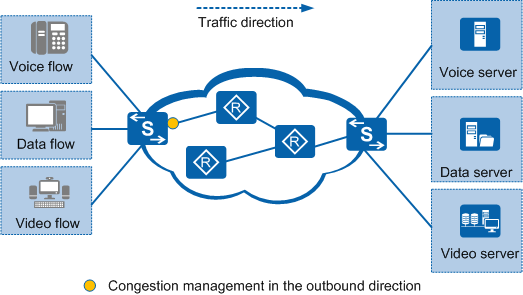
Congestion management is often deployed in QoS applications to schedule different services based on priorities.
On a network, when multiple services compete for the same resources (such as the bandwidth and buffer), traffic congestion may occur. Consequently, high-priority services may not be processed in a timely manner.
Figure 2 shows a network implementing congestion management. Packets are sent to different queues based on their priorities. To implement differentiated services, different scheduling modes are set in the outbound direction.