Overview of VLAN Termination
Definition
VLAN termination is a VLAN tag processing mechanism. VLAN termination enables a device to identify VLAN tags and remove single or double VLAN tags from received packets. It then forwards the packets over Layer 3 or takes other actions as required. These VLAN tags are only useful before termination, and are not used in Layer 3 forwarding or other processing.
- Removes single or double VLAN tags from the packets received on interfaces, and then selects an appropriate action such as forwarding the packets over Layer 3.
- Adds VLAN tags to the packets that will be sent out through interfaces.
Classification
Depending on the selected method for VLAN tagged packets processing, VLAN termination has the following sub-functions:
- Dot1q termination: The device removes the outer VLAN tag from any received single-tagged or double-tagged packets, and adds a VLAN tag to the packets to be sent by an interface.
- QinQ termination: The device removes double VLAN tags from any received double-tagged packets, and adds double VLAN tags to the packets to be sent by an interface.
Generally, VLAN termination is configured on sub-interfaces. A sub-interface that terminates single tags in packets is called a Dot1q termination sub-interface, and a sub-interface that terminates double tags in packets is called a QinQ termination sub-interface.

Purpose
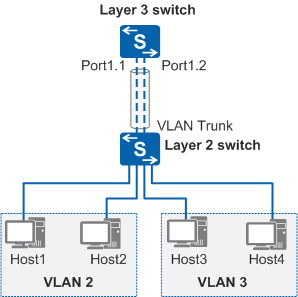
After VLANs are assigned on a network, hosts in the same VLAN can communicate with each other over Layer 2 but in different VLANs cannot communicate with each other. You can use VLANIF interfaces on a Layer 3 switch to implement inter-VLAN Layer 3 connectivity, but this encounters the following problem. As shown in Figure 1, when a Layer 3 switch uses only one Layer 3 Ethernet interface to connect to users or a network, this interface needs to transmit packets from multiple VLANs. A VLANIF interface cannot provide this function. To solve this problem, you can virtualize a Layer 3 Ethernet interface into multiple logical sub-interfaces with the Layer 3 Ethernet interface as the main interface.
However, a Layer 3 Ethernet sub-interface treats received VLAN packets as invalid packets and discards them; therefore, VLAN termination needs to be configured on the Layer 3 Ethernet sub-interface so that the sub-interface can remove VLAN tags from packets.