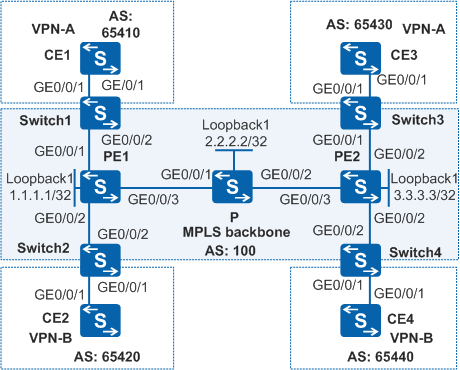
Example for Connecting QinQ Termination Sub-interfaces to an L3VPN
Networking Requirements
In the network example shown in Figure 1, CE1 and CE3 belong to VPN-A, and CE2 and CE4 belong to VPN-B. The VPN targets of VPN-A and VPN-B are 111:1 and 222:2 respectively. Users in different VPNs cannot communicate with each other.
Selective QinQ needs to be configured on the interfaces connected to CEs so that the Switch adds the VLAN tags specified by the carrier to the packets sent from CEs.
When the Switch is connected to multiple CEs, the Switch can add the same VLAN tag to the packets from different CEs, thereby saving VLAN IDs on the public network.
Switch |
Interface |
Layer 3 Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|
PE1 |
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 |
GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
- |
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 |
GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1 |
10.2.1.2/24 |
- |
GigabitEthernet0/0/3 |
VLANIF 30 |
7.7.7.7/24 |
PE2 |
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 |
GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1 |
10.3.1.2/24 |
- |
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 |
GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1 |
10.4.1.2/24 |
- |
GigabitEthernet0/0/3 |
VLANIF 60 |
6.6.6.7/24 |
P |
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 |
VLANIF 30 |
7.7.7.8/24 |
- |
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 |
VLANIF 60 |
6.6.6.6/24 |
CE1 |
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 |
VLANIF 10 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
CE2 |
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 |
VLANIF 20 |
10.2.1.1/24 |
CE3 |
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 |
VLANIF 10 |
10.3.1.1/24 |
CE4 |
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 |
VLANIF 20 |
10.4.1.1/24 |
Configuration Roadmap
Configure VPN instances on PEs connected to CEs on the backbone network, bind interfaces connected to CEs to VPN instances, and assign IP addresses to interfaces connected to CEs.
Configure OSPF on PEs to implement interworking between PEs.
Configure basic MPLS functions and MPLS LDP, and set up MPLS LSPs.
Configure the Multi-protocol Extensions for Interior Border Gateway Protocol (MP-IBGP) on PEs to exchange VPN routing information.
Configure EBGP on CEs and PEs to exchange VPN routing information.
Configure QinQ termination sub-interfaces on PE interfaces connected to the Switch, so that the QinQ termination sub-interfaces can connect to the L3VPN.
Configure selective QinQ on Switch interfaces connected to CEs.

VLAN termination sub-interfaces cannot be created on a VCMP client.
Procedure
- Configure selective QinQ on interfaces of the Switch and specify the VLANs allowed by the interfaces.
# Configure Switch1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Switch1 [Switch1] vlan 100 [Switch1-vlan100] quit [Switch1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 [Switch1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type hybrid [Switch1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port hybrid tagged vlan 100 [Switch1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [Switch1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 [Switch1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type hybrid [Switch1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] qinq vlan-translation enable [Switch1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid untagged vlan 100 [Switch1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port vlan-stacking vlan 10 stack-vlan 100 [Switch1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Configure Switch2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Switch2 [Switch2] vlan 200 [Switch2-vlan200] quit [Switch2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 [Switch2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type hybrid [Switch2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port hybrid tagged vlan 200 [Switch2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [Switch2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 [Switch2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type hybrid [Switch2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] qinq vlan-translation enable [Switch2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid untagged vlan 200 [Switch2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port vlan-stacking vlan 20 stack-vlan 200 [Switch2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Configure Switch3.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Switch3 [Switch3] vlan 100 [Switch3-vlan100] quit [Switch3] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 [Switch3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type hybrid [Switch3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port hybrid tagged vlan 100 [Switch3-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [Switch3] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 [Switch3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type hybrid [Switch3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] qinq vlan-translation enable [Switch3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid untagged vlan 100 [Switch3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port vlan-stacking vlan 10 stack-vlan 100 [Switch3-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
# Configure Switch4.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname Switch4 [Switch4] vlan 200 [Switch4-vlan200] quit [Switch4] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 [Switch4-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type hybrid [Switch4-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port hybrid tagged vlan 200 [Switch4-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [Switch4] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 [Switch4-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type hybrid [Switch4-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] qinq vlan-translation enable [Switch4-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid untagged vlan 200 [Switch4-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port vlan-stacking vlan 20 stack-vlan 200 [Switch4-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit
- Configure an IGP, for example, OSPF, on the MPLS backbone network so that PEs and the P can communicate with each other.
# Configure PE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [PE1] router id 1.1.1.1 [PE1] interface loopback 1 [PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32 [PE1-LoopBack1] quit [PE1] vlan batch 30 [PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port link-type hybrid [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port hybrid pvid vlan 30 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port hybrid untagged vlan 30 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit [PE1] interface vlanif 30 [PE1-Vlanif30] ip address 7.7.7.7 24 [PE1-Vlanif30] quit [PE1] ospf [PE1-ospf-1] area 0 [PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 7.7.7.0 0.0.0.255 [PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 [PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [PE1-ospf-1] quit
# Configure P.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname P [P] router id 2.2.2.2 [P] interface loopback 1 [P-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.2 32 [P-LoopBack1] quit [P] vlan batch 30 60 [P] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type hybrid [P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid pvid vlan 30 [P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid untagged vlan 30 [P-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [P] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/2 [P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type hybrid [P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port hybrid pvid vlan 60 [P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port hybrid untagged vlan 60 [P-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [P] interface vlanif 30 [P-Vlanif30] ip address 7.7.7.8 24 [P-Vlanif30] quit [P] interface vlanif 60 [P-Vlanif60] ip address 6.6.6.6 24 [P-Vlanif60] quit [P] ospf [P-ospf-1] area 0 [P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 7.7.7.0 0.0.0.255 [P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 6.6.6.0 0.0.0.255 [P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 [P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [P-ospf-1] quit
# Configure PE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname PE2 [PE2] router id 3.3.3.3 [PE2] interface loopback 1 [PE2-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.3 32 [PE2-LoopBack1] quit [PE2] vlan batch 60 [PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/3 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port link-type hybrid [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port hybrid pvid vlan 60 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] port hybrid untagged vlan 60 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/3] quit [PE2] interface vlanif 60 [PE2-Vlanif60] ip address 6.6.6.7 24 [PE2-Vlanif60] quit [PE2] ospf [PE2-ospf-1] area 0 [PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 6.6.6.0 0.0.0.255 [PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 [PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [PE2-ospf-1] quit
After the configuration is complete, PE1, P, and PE2 can establish OSPF neighbor relationships. Run the display ospf peer command. You can see that the OSPF neighbor relationship status is Full. Run the display ip routing-table command. You can see that the PEs learn each other's routes to the Loopback1 interface.
The following is the display on PE1:
[PE1] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Tables: Public Destinations : 8 Routes : 8 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 LoopBack1 2.2.2.2/32 OSPF 10 1 D 7.7.7.8 Vlanif30 3.3.3.3/32 OSPF 10 2 D 7.7.7.8 Vlanif30 6.6.6.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 7.7.7.8 Vlanif30 7.7.7.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 7.7.7.7 Vlanif30 7.7.7.7/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vlanif30 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0[PE1] display ospf peer OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 1.1.1.1 Neighbors Area 0.0.0.0 interface 7.7.7.7(Vlanif30)'s neighbors Router ID: 2.2.2.2 Address: 7.7.7.8 State: Full Mode:Nbr is Master Priority: 1 DR: 7.7.7.8 BDR: 7.7.7.7 MTU: 0 Dead timer due in 37 sec Retrans timer interval: 5 Neighbor is up for 00:00:20 Authentication Sequence: [ 0 ] - Configure basic MPLS functions, enable MPLS LDP, and establish LDP LSPs on the MPLS backbone network.
# Configure PE1.
[PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [PE1] mpls [PE1-mpls] quit [PE1] mpls ldp [PE1-mpls-ldp] quit [PE1] interface vlanif 30 [PE1-Vlanif30] mpls [PE1-Vlanif30] mpls ldp [PE1-Vlanif30] quit
# Configure P.
[P] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 [P] mpls [P-mpls] quit [P] mpls ldp [P-mpls-ldp] quit [P] interface vlanif 30 [P-Vlanif30] mpls [P-Vlanif30] mpls ldp [P-Vlanif30] quit [P] interface vlanif 60 [P-Vlanif60] mpls [P-Vlanif60] mpls ldp [P-Vlanif60] quit
# Configure PE2.
[PE2] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 [PE2] mpls [PE2-mpls] quit [PE2] mpls ldp [PE2-mpls-ldp] quit [PE2] interface vlanif 60 [PE2-Vlanif60] mpls [PE2-Vlanif60] mpls ldp [PE2-Vlanif60] quit
After the configuration is complete, LDP sessions can be set up between PE1 and the P, and between the P and PE2. Run the display mpls ldp session command. You can see that the Status field is Operational. Run the display mpls ldp lsp command to view the MPLS LDP configuration.
The following is the display on PE1:
[PE1] display mpls ldp session LDP Session(s) in Public Network Codes: LAM(Label Advertisement Mode), SsnAge Unit(DDDD:HH:MM) A '*' before a session means the session is being deleted. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ PeerID Status LAM SsnRole SsnAge KASent/Rcv ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 2.2.2.2:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:15:29 3717/3717 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ TOTAL: 1 session(s) Found.
[PE1] display mpls ldp lsp LDP LSP Information ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Flag after Out IF: (I) - LSP Is Only Iterated by RLFA ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- DestAddress/Mask In/OutLabel UpstreamPeer NextHop OutInterface ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1.1.1.1/32 3/NULL 2.2.2.2 127.0.0.1 InLoop0 *1.1.1.1/32 Liberal/1024 DS/2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2/32 NULL/3 - 7.7.7.8 Vlanif30 2.2.2.2/32 1024/3 2.2.2.2 7.7.7.8 Vlanif30 3.3.3.3/32 NULL/1025 - 7.7.7.8 Vlanif30 3.3.3.3/32 1025/1025 2.2.2.2 7.7.7.8 Vlanif30 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- TOTAL: 5 Normal LSP(s) Found. TOTAL: 1 Liberal LSP(s) Found. TOTAL: 0 Frr LSP(s) Found. A '*' before an LSP means the LSP is not established A '*' before a Label means the USCB or DSCB is stale A '*' before a UpstreamPeer means the session is stale A '*' before a DS means the session is stale A '*' before a NextHop means the LSP is FRR LSP - Configure a VPN instance on each PE and connect CEs to PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna [PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] route-distinguisher 100:1 [PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 both [PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [PE1] ip vpn-instance vpnb [PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb] route-distinguisher 100:2 [PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb-af-ipv4] vpn-target 222:2 both [PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb-af-ipv4] quit [PE1-vpn-instance-vpnb] quit [PE1] vcmp role silent [PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type hybrid [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.1 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1] qinq termination pe-vid 100 ce-vid 10 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1] arp broadcast enable [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1] quit [PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type hybrid [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2.1 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1] qinq termination pe-vid 200 ce-vid 20 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1] ip binding vpn-instance vpnb [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1] ip address 10.2.1.2 24 [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1] arp broadcast enable [PE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[PE2] ip vpn-instance vpna [PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] route-distinguisher 200:1 [PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 both [PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [PE2] ip vpn-instance vpnb [PE2-vpn-instance-vpnb] route-distinguisher 200:2 [PE2-vpn-instance-vpnb-af-ipv4] vpn-target 222:2 both [PE2-vpn-instance-vpnb-af-ipv4] quit [PE2-vpn-instance-vpnb] quit [PE2] vcmp role silent [PE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type hybrid [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [PE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1.1 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1] qinq termination pe-vid 100 ce-vid 10 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1] ip address 10.3.1.2 24 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1] arp broadcast enable [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1] quit [PE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] port link-type hybrid [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2] quit [PE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2.1 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1] qinq termination pe-vid 200 ce-vid 20 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1] ip binding vpn-instance vpnb [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1] ip address 10.4.1.2 24 [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1] arp broadcast enable [PE2-GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1] quit
# Assign IP addresses to interfaces on CE1 according to Figure 1. The configurations of CE2, CE3, and CE4 are the same as the configuration of CE1, and are not mentioned here.
<HUAWEI> system-view [HUAWEI] sysname CE1 [CE1] vlan batch 10 [CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 [CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port link-type hybrid [CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid pvid vlan 10 [CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] port hybrid tagged vlan 10 [CE1-GigabitEthernet0/0/1] quit [CE1] interface vlanif 10 [CE1-Vlanif10] ip address 10.1.1.1 24 [CE1-Vlanif10] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display ip vpn-instance verbose command on PEs to check the VPN instance configuration. Each PE can successfully ping its connected CE.

If multiple interfaces of a PE are bound to the same VPN instance, run the ping -vpn-instance vpn-instance-name -a source-ip-address dest-ip-address command with -a source-ip-address specified to ping the CE connected to the remote PE. Otherwise, the ping operation may fail.
The following is the display on PE1:
[PE1] display ip vpn-instance verbose Total VPN-Instances configured : 2 Total IPv4 VPN-Instances configured : 2 Total IPv6 VPN-Instances configured : 0 VPN-Instance Name and ID : vpna, 1 Interfaces : Gigabitethernet0/0/1.1 Address family ipv4 Create date : 2013-08-28 21:01:00+00:00 Up time : 0 days, 22 hours, 24 minutes and 53 seconds Route Distinguisher : 100:1 Export VPN Targets : 111:1 Import VPN Targets : 111:1 Label Policy : label per instance Per-Instance Label : 4098 Log Interval : 5 VPN-Instance Name and ID : vpnb, 2 Interfaces : Gigabitethernet0/0/2.1 Address family ipv4 Create date : 2013-08-28 21:01:00+00:00 Up time : 0 days, 22 hours, 24 minutes and 53 seconds Route Distinguisher : 100:2 Export VPN Targets : 222:2 Import VPN Targets : 222:2 Label Policy : label per instance Per-Instance Label : 4099 Log Interval : 5
[PE1] ping -vpn-instance vpna 10.1.1.1 PING 10.1.1.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=5 ms Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=3 ms Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=3 ms Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=3 ms Reply from 10.1.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=16 ms --- 10.1.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 3/6/16 ms - Set up EBGP peer relationships between PEs and CEs and configure CEs to import VPN routes.
# Configure CE1. The configurations of CE2, CE3, and CE4 are the same as the configuration of CE1, and are not mentioned here.
[CE1] bgp 65410 [CE1-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 [CE1-bgp] import-route direct
# Configure PE1. The configuration of PE2 is the same as the configuration of PE1, and is not mentioned here.
[PE1] bgp 100 [PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna [PE1-bgp-vpna] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410 [PE1-bgp-vpna] import-route direct [PE1-bgp-vpna] quit [PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpnb [PE1-bgp-vpnb] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65420 [PE1-bgp-vpnb] import-route direct [PE1-bgp-vpnb] quit [PE1-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance peer command on PEs. You can see that BGP peer relationships between PEs and CEs have been established and are in the Established state.
The following is the peer relationship between PE1 and CE1:
[PE1] display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance vpna peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 VPN-Instance vpna, Router ID 1.1.1.1: Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 10.1.1.1 4 65410 11 9 0 00:07:25 Established 1
- Set up an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[PE1] bgp 100 [PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 [PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface loopback 1 [PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 3.3.3.3 enable [PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure PE2.
[PE2] bgp 100 [PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 [PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 1 [PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [PE2-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, run the display bgp peer or display bgp vpnv4 all peer command on PEs. You can see that the BGP peer relationships have been established between the PEs.
[PE1] display bgp peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 3.3.3.3 4 100 12 6 0 00:02:21 Established 0
[PE1] display bgp vpnv4 all peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 3 Peers in established state : 3 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 3.3.3.3 4 100 12 18 0 00:09:38 Established 0 Peer of IPv4-family for vpn instance : VPN-Instance vpna, Router ID 1.1.1.1: 10.1.1.1 4 65410 25 25 0 00:17:57 Established 1 VPN-Instance vpnb, Router ID 1.1.1.1: 10.2.1.1 4 65420 21 22 0 00:17:10 Established 1
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display ip routing-table vpn-instance command on a PE. You can view the routes to the remote CE.
The following is the display on PE1:
[PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpna Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Tables: vpna Destinations : 3 Routes : 3 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 Gigabitethernet0/0/1.1 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Gigabitethernet0/0/1.1 10.3.1.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 3.3.3.3 Vlanif30
[PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpnb Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Tables: vpnb Destinations : 3 Routes : 3 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.2.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.2.1.2 Gigabitethernet0/0/2.1 10.2.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Gigabitethernet0/0/2.1 10.4.1.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 3.3.3.3 Vlanif30
CEs in the same VPN can successfully ping each other but CEs in different VPNs cannot.
For example, CE1 can successfully ping CE3 at 10.3.1.1 but cannot ping CE4 at 10.4.1.1.
[CE1] ping 10.3.1.1 PING 10.3.1.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 10.3.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=253 time=72 ms Reply from 10.3.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=253 time=34 ms Reply from 10.3.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=253 time=50 ms Reply from 10.3.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=253 time=50 ms Reply from 10.3.1.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=253 time=34 ms --- 10.3.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 34/48/72 ms[CE1] ping 10.4.1.1 PING 10.4.1.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Request time out Request time out Request time out Request time out Request time out --- 10.4.1.1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 0 packet(s) received 100.00% packet loss
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # router id 1.1.1.1 # vcmp role silent # vlan batch 30 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity # ip vpn-instance vpnb ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:2 vpn-target 222:2 export-extcommunity vpn-target 222:2 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif30 ip address 7.7.7.7 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1 qinq termination pe-vid 100 ce-vid 10 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 arp broadcast enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type hybrid # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1 qinq termination pe-vid 200 ce-vid 20 ip binding vpn-instance vpnb ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 arp broadcast enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type hybrid port hybrid pvid vlan 30 port hybrid untagged vlan 30 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410 import-route direct # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpnb peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65420 import-route direct # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 7.7.7.0 0.0.0.255 # return
P configuration file
# sysname P # router id 2.2.2.2 # vlan batch 30 60 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif30 ip address 7.7.7.8 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Vlanif60 ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid port hybrid pvid vlan 30 port hybrid untagged vlan 30 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type hybrid port hybrid pvid vlan 60 port hybrid untagged vlan 60 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 7.7.7.0 0.0.0.255 network 6.6.6.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # router id 3.3.3.3 # vcmp role silent # vlan batch 60 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:1 vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity # ip vpn-instance vpnb ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:2 vpn-target 222:2 export-extcommunity vpn-target 222:2 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Vlanif60 ip address 6.6.6.7 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1 qinq termination pe-vid 100 ce-vid 10 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.3.1.2 255.255.255.0 arp broadcast enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type hybrid # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2.1 qinq termination pe-vid 200 ce-vid 20 ip binding vpn-instance vpnb ip address 10.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 arp broadcast enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/3 port link-type hybrid port hybrid pvid vlan 60 port hybrid untagged vlan 60 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna peer 10.3.1.1 as-number 65430 import-route direct # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpnb peer 10.4.1.1 as-number 65440 import-route direct # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 6.6.6.0 0.0.0.255 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # vlan batch 10 # interface Vlanif10 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid port hybrid pvid vlan 10 port hybrid tagged vlan 10 # bgp 65410 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 10.1.1.2 enable # return
CE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # vlan batch 20 # interface Vlanif20 ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid port hybrid pvid vlan 20 port hybrid tagged vlan 20 bgp 65420 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 10.2.1.2 enable # return
CE3 configuration file
# sysname CE3 # vlan batch 10 # interface Vlanif10 ip address 10.3.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid port hybrid pvid vlan 10 port hybrid tagged vlan 10 # bgp 65430 peer 10.3.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 10.3.1.2 enable # return
CE4 configuration file
# sysname CE4 # vlan batch 20 # interface Vlanif20 ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid port hybrid pvid vlan 20 port hybrid tagged vlan 20 # bgp 65440 peer 10.4.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 10.4.1.2 enable # return
Switch1 configuration file
# sysname Switch1 # vlan batch 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid qinq vlan-translation enable port hybrid untagged vlan 100 port vlan-stacking vlan 10 stack-vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type hybrid port hybrid tagged vlan 100 # return
Switch2 configuration file
# sysname Switch2 # vlan batch 200 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid qinq vlan-translation enable port hybrid untagged vlan 200 port vlan-stacking vlan 20 stack-vlan 200 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type hybrid port hybrid tagged vlan 200 # return
Switch3 configuration file
# sysname Switch3 # vlan batch 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid qinq vlan-translation enable port hybrid untagged vlan 100 port vlan-stacking vlan 10 stack-vlan 100 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type hybrid port hybrid tagged vlan 100 # return
Switch4 configuration file
# sysname Switch4 # vlan batch 200 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 port link-type hybrid qinq vlan-translation enable port hybrid untagged vlan 200 port vlan-stacking vlan 20 stack-vlan 200 # interface GigabitEthernet0/0/2 port link-type hybrid port hybrid tagged vlan 200 # return