Overview of VLANs
Definition
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) are used to divide a physical LAN into multiple broadcast domains to isolate services with the aim of improving the security and management of the network.
Purpose
In the early stage, an Ethernet network implements data communication over shared media based on Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD). When an Ethernet network has a large number of hosts, both collisions and broadcast storms become a serious problem, affecting network performance and in some cases causing the network to completely break down. Although using switches to connect LANs can prevent collisions, they cannot isolate broadcast packets or improve network quality.
A physical LAN can be logically segmented into multiple VLANs to isolate broadcast domains. Hosts within a VLAN can directly communicate only with other hosts in the same VLAN and must use a router to communicate with hosts in other VLANs.
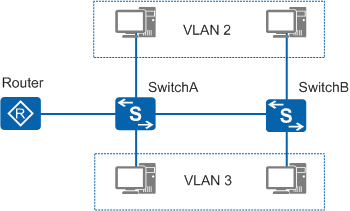
Figure 1 shows a simple VLAN networking environment. Two switches are deployed in different locations (for example, on different floors of a building). Each switch is connected to two PCs belonging to different VLANs, which may belong to different entities or companies.
Benefits
- Limit the scope of broadcast domains: The scope of broadcast domains is limited to conserve bandwidth and improve network efficiency.
- Enhance LAN security: Packets from different VLANs are transmitted separately, preventing hosts in a VLAN from communicating directly with hosts in another VLAN.
- Improve network robustness: A fault in one VLAN does not affect hosts in other VLANs.
- Allow for flexible groups: By leveraging VLANs, it is possible to group hosts in different geographical locations, simplifying network construction and maintenance.