Using VLAN Assignment to Implement Layer 2 Isolation
Interface-based VLAN Assignment
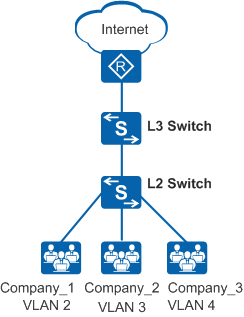
As shown in Figure 1, there are multiple companies in a building. These companies share network resources to reduce costs. Networks of the companies connect to different interfaces of the same Layer 2 switch and access the Internet through an egress.
To isolate services and ensure service security of different companies, add interfaces connected to the companies to different VLANs. Each company has a virtual router and each VLAN is a virtual work group.
MAC Address-based VLAN Assignment
As shown in Figure 2, a company has two office areas that connect to the company's network through Switch_2 and Switch_3, respectively. Employees often move between the two office areas.
To enable employees to access network resources such as servers after they move between different office areas, configure MAC address-based VLAN assignment on Switch_2 and Switch_3. As long as the MAC address of User_1 remains unchanged, the VLAN of the user remains unchanged and they can still access the company's network resources after changing the location.
IP Subnet-based VLAN Assignment
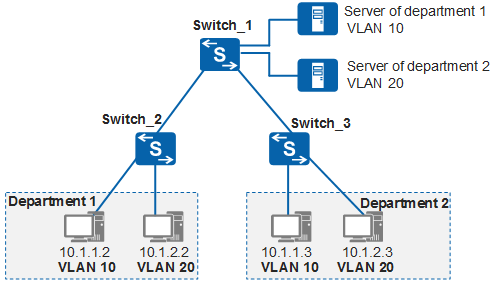
As shown in Figure 3, a company has two departments: departments 1 and 2. The two departments are assigned fixed IP network segments. The employees often move between locations, but the company requires that their network resource access rights remain unchanged.
To ensure that employees retain access to network resources after changing locations, configure IP subnet-based VLAN assignment on the company's central switch. Different network segments of servers are assigned to different VLANs to isolate data flows of different application services, improving security.