(Optional) Configuring Flow Label-based Load Balancing
Context
Flow label-based load balancing enables Layer 2 virtual private network (L2VPN) data flows to be forwarded along different paths based on flow labels.
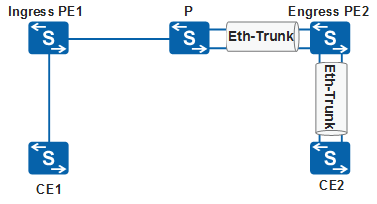
In an L2VPN scenario shown in Figure 1, the interfaces connecting the P device and PE2 as well as connecting PE2 and the CE are added to Eth-Trunks. Service flows from the same L2VPN use the same inner private label and outer public label. If label-based load balancing is used, the service flows cannot be load balanced along links in an Eth-Trunk because the service flows have the same hash factor. Flow labels can solve this problem. Ingress PE1 distributes a flow label to each service flow to uniquely identify this service flow. This flow label is stored in the innermost layer in the label stack on Ingress PE1. Egress PE2 can pop out flow labels. After flow labels are assigned, the P device and Egress PE2 can load balance flows in an Eth-Trunk based on the flow labels.

Currently, only the following techniques support flow label-based load balancing in an L2VPN scenario: static virtual circuit (SVC) and Martini virtual leased line (VLL), dynamic pseudo wire emulation edge-to-edge (PWE3), and Martini virtual private LAN service (VPLS)