Configuring an IPv6 VXLAN Tunnel
Context
When configuring VXLAN on a device, you need to configure related information for IPv6 VXLAN tunnel establishment on an uplink interface.
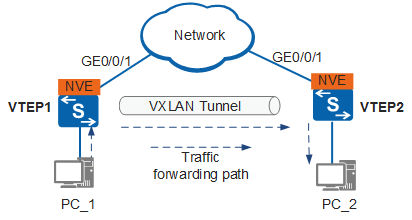
An IPv6 VXLAN tunnel is established based on the IPv6 addresses of two VXLAN Tunnel Endpoints (VTEPs). Therefore, you need to configure the source VTEP IPv6 address and destination VTEP IPv6 address on the devices on both ends of a tunnel.
Take VTEP1 in Figure 1 as an example. The following describes the configurations required for establishment of an IPv6 VXLAN tunnel:
- Source VTEP IPv6 address: source IPv6 address in an IPv6 VXLAN packet, that is, IPv6 address of GE0/0/1 on VTEP1
- Destination VTEP IPv6 address: destination IPv6 address in an IPv6 VXLAN packet, that is, IPv6 address of GE0/0/1 on VTEP2

You need to run the vni head-end peer-list command to configure the corresponding VTEP address even if the source VTEP matches only one destination VTEP.
Run the ping command to check whether a reachable route exists between two ends of the tunnel. If there is a reachable route, the tunnel can be established and packets can be normally forwarded. If the two devices have a route to each other but the route is unreachable, the tunnel can still go Up but packets cannot be forwarded.
If a switch uses static routes to forward traffic at the tunnel side, you are advised to configure BFD for static routes. Routes then can be deleted promptly when a link failure occurs. This configuration prevents VXLAN packet loss that occurs because routes are unreachable but the tunnel is still Up.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run bridge-domain bd-id
The BD view is displayed.
- Run vxlan vni vni-id
A VNI is configured for the BD.
By default, no VNI is associated with a BD.
- Run quit
Exit from the BD view and return to the system view.
- Run interface nve nve-number
An NVE interface is created, and the NVE interface view is displayed.
- Run source ipv6-address
An IPv6 address is configured for the source VTEP.
By default, no IPv6 address is configured for a source VTEP.
- Run vni vni-id head-end peer-list ipv6-address &<1-10>
An ingress replication list is configured.
By default, no ingress replication list is configured for any VNI.
After the ingress of a VXLAN tunnel receives broadcast, unknown unicast, and multicast (BUM) packets, it replicates these packets and sends a copy to each VTEP in the ingress replication list. The ingress replication list is a collection of remote VTEP IPv6 addresses to which the ingress of a VXLAN tunnel should send replicated BUM packets to.

BUM packet forwarding is implemented only using ingress replication. To establish a VXLAN tunnel between a Huawei device and a non-Huawei device, ensure that the non-Huawei device also has ingress replication configured. Otherwise, communication fails.
- Run quit
Exit from the NVE interface view and return to the system view.
- (Optional) Run vxlan tunnel-status track exact-route
Subscription to the status of the exact route to a VXLAN tunnel destination is enabled.
By default, subscription to the status of the exact route to a VXLAN tunnel destination is disabled.
By default, if the source IPv6 address of a VXLAN tunnel is reachable using a exact and the network segment where the destination IPv6 address belongs is reachable using a route, this VXLAN tunnel is considered Up. In real-world networking, there may be multiple destination addresses on the same network segment. If the network segment is considered reachable because one of the destination addresses is reachable, the tunnel status is reported incorrectly when an IPv6 address on this network segment becomes unreachable. As a result, network faults cannot be discovered in a timely manner. To address this issue, run the vxlan tunnel-status track exact-route command to enable subscription to the status of the exact route to a VXLAN tunnel destination. Subsequently, the VXLAN tunnel is considered Up only when the destination VTEP is reachable using a exact route.