Managing an AP's Wired Interface
Context
Managing an AP's wired interface includes configuring AP wired interface parameters and link layer parameters.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run wlan
The WLAN view is displayed.
- Run wired-port-profile name profile-name
An AP wired port profile is created, and the AP wired port profile view is displayed.
By default, the system provides the AP wired port profile default.
- Configure parameters for an AP's wired interface. Run the following commands as required.
Run the eth-trunk trunk-id command to add an AP's wired interface to an Eth-Trunk.
By default, an AP interface is not added to any Eth-Trunk.
To improve the connection reliability and increase the bandwidth, you can run this command to bind multiple interfaces into an Eth-Trunk.

APs that have only one physical uplink network interface do not support this command.
The physical interface to be added to an Eth-Trunk cannot have other configurations. Before adding a physical interface to an Eth-Trunk, clear all configurations on it except the interface status, descriptions, LLDP function, and alarm function for CRC errors.
Run the stp enable command to enable STP on an AP's wired interface.
By default, STP is disabled on an AP's wired interface.
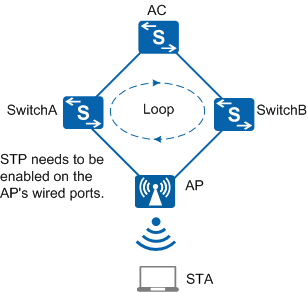
STP on the AP's wired interfaces takes effect only when the AP forms a single loop with wired devices. As shown in Figure 1, the AC, SwitchA, SwitchB, and AP form a loop. To break the loop, configure STP on the AP's wired interfaces. After STP is configured, the AP's wired interfaces are engaged in STP calculation of the loop and will be blocked based on the calculation results.
The STP cost on Huawei switches (including ACs) complies with 802.1t, while the STP cost on Huawei APs complies with 802.1d. When a Huawei AP is connected to a Huawei switch or an AC and STP is enabled on the AP, run the stp pathcost-standard dot1d-1998 command in the system view of the switch or AC to set the correct STP cost. Incorrect STP cost may block the link between the AP and AC.
Run the mode { root | endpoint | middle } command to configure a working mode for an AP's wired interface.
By default,- On a common AP (excluding AirEngine series APs): Its GE interfaces work in root mode, Ethernet interfaces in endpoint mode, and Eth-Trunk interfaces in root mode.
- On a central AP (excluding AirEngine series APs): Its uplink 10GE/GE interfaces in root mode and downlink GE interfaces work in middle mode.
- On an R230D: Its Ethernet interface works in root mode.
- On an R240D and AP2051DN-L-S: Their Ethernet interfaces work in endpoint mode and GE interfaces in root mode.
- On an R250D, R250D-E, AP2050DN, AP5510-W-GP, AP2050DN-S, AP2050DN-E, AP2051DN, AP2051DN-S, AP2051DN-E, R251D, and R251D-E: Their uplink GE interfaces work in root mode and downlink GE interfaces in endpoint mode.
- On an R450D: Its GE interface works in root mode.
- AirEngine 5760-10: Its GE interface works in root mode.
- On an AirEngine 8760-X1-PRO, AirEngine 6760-X1, AirEngine 6760-X1E, and AirEngine 5760-51: Its 10GE/5GE/GE interfaces work in root and Eth-Trunk interfaces work in root mode.
- On an AirEngine 8760R-X1, AirEngine 8760R-X1E, AirEngine 6760R-51, and AirEngine 6760R-51E: Its 10GE/5GE interfaces work in root, GE interfaces in endpoint, and Eth-Trunk interfaces in root mode.
- On an AirEngine 5760-22W and AirEngine 5760-22WD: Its 10GE/2.5GE interfaces work in root mode and GE interfaces work in endpoint mode.
- On an AirEngine 9700D-M: Its uplink 10GE interfaces in root mode and downlink GE interfaces work in middle mode.
When working as an uplink interface to connect to an AC, an AP's wired interface must work in root mode. In root mode, the AP's wired interface automatically joins service VLANs and user-specific VLANs (for example, VLANs assigned by the RADIUS server).
When working as a downlink interface to connect to a wired terminal, the AP's wired interface must work in endpoint mode. In endpoint mode, the AP's wired interface does not join any VLAN by default.

The AP's wired interface supports user isolation in endpoint mode, but not in root or middle mode.
Run the dhcp trust port command to enable a DHCP trusted port on an AP's wired interface.
By default, the DHCP trusted interface is enabled on the AP's uplink interface in the AP wired port profile view.
This command takes effect only on the AP's uplink interface.
Before WLAN services are delivered to an AP, run the dhcp trust port command in the AP wired port profile view. After the command is run, the AP receives the DHCP OFFER, ACK, and NAK packets sent by the authorized DHCP server and forwards the packets to STAs so that the STAs can obtain valid IP addresses and go online.
Run the nd trust port command to enable an ND trusted port on an AP's wired interface.
By default, the ND trusted interface is disabled on an AP
Before WLAN services are delivered to an AP, run the nd trust port command in the AP wired port profile view. After the command is run, the AP receives the ND OFFER, ACK, and NAK packets sent by the authorized ND server and forwards the packets to STAs so that the STAs can obtain valid IPv6 addresses and go online.

If a bogus ND server is deployed at the user side, STAs may obtain incorrect IPv6 addresses and network configuration parameters and cannot communicate properly. After the nd trust port command is executed in the VAP profile view, an AP discards the ND OFFER, ACK, and NAK packets sent by the bogus ND server and the IPv6 address of the unauthorized ND server. For details, see Configuring Defense Against Bogus ND Server Attacks.
Run the learn-client-address { ipv4 | ipv6 } enable command to enable terminal address learning on an AP's wired interface.
By default, terminal address learning is disabled on an AP's wired interface.
After terminal address learning is enabled on an AP's wired interface, if a wired terminal connected to the AP wired interface successfully obtains an IP address, the AP automatically reports the IP address of the terminal to the AC, helping to maintain the ARP binding entries of wired terminals.
This configuration takes effect only on AP's wired interfaces working in endpoint mode.
Run the ipsg enable command to enable IP source guard (IPSG) on an AP's wired interface.
By default, IPSG is disabled on an AP's wired interface.
Attackers often use packets with the source IP addresses or MAC addresses of authorized users to access or attack networks. As a result, authorized users cannot obtain stable and secure network services. You can enable the IPSG function to prevent the situation.
To make the configuration take effect, terminal address learning must be enabled on the AP's wired interface using the learn-client-address enable command.
Run the dai enable command to enable dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) on an AP's wired interface.
By default, DAI is disabled on an AP's wired interface.
You can enable DAI using this command to prevent Man in The Middle (MITM) attacks and theft on authorized user information. When a device receives an ARP packet, it compares the source IP address, source MAC address, interface number, and VLAN ID of the ARP packet with DHCP snooping binding entries. If the ARP packet matches a binding entry, the device allows the packet to pass through. If the ARP packet does not match any binding entry, the device discards the packet.
To make the configuration take effect, terminal address learning must be enabled on the AP's wired interface using the learn-client-address enable command.
Run the traffic-optimize { broadcast-suppression | multicast-suppression | unicast-suppression } packets packets-rate command to set the maximum volume of broadcast, multicast, or unknown unicast traffic on an AP's wired interface.
By default, the volume of broadcast, multicast, or unknown unicast traffic is not suppressed on an AP's wired interface.
When a large number of broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast packets are transmitted on a network, a lot of network resources are occupied, and services on the network are affected. When the traffic volume of broadcast, multicast, and unknown unicast packets reaches the maximum on an AP's wired interface, the system discards excess packets to control the traffic volume in a proper range and prevent flooding attacks.
Run the stp auto-shutdown enable command to enable the STP-triggered port shutdown function on an AP's wired interface.
By default, the STP-triggered port shutdown function is disabled on an AP's wired interface.
After the STP-triggered port shutdown function is enabled, the AP automatically shuts down the interface when STP detects a loop. The AP will periodically recover the interface and re-executes STP detection. If the loop still exists on the interface, the AP shuts down the interface again. If the loop is removed, the AP reports a clear alarm to the network management system (NMS).
To make the configuration take effect, the stp enable command must be run first.
Run the stp auto-shutdown recovery-time recovery-time command to set an auto-recovery interval for an AP's wired interface on which the STP-triggered port shutdown function is enabled.
By default, the auto-recovery interval is 600s.
After the STP-triggered port shutdown function is enabled, the AP automatically shuts down the interface when STP detects a loop. The AP will periodically recover the interface and re-executes STP detection. If the loop still exists on the interface, the AP shuts down the interface again. If the loop is removed, the AP reports a clear alarm to the network management system (NMS).
To make the configuration take effect, the stp auto-shutdown enable command must be run first.
Run the igmp-snooping enable command to enable IGMP snooping on an AP's wired interface.
By default, IGMP snooping is disabled on an AP's wired interface.
IGMP snooping is a basic Layer 2 multicast function that forwards and controls multicast traffic at the data link layer. IGMP snooping runs on a Layer 2 device and analyzes IGMP messages exchanged between a Layer 3 device and hosts to set up and maintain a Layer 2 multicast forwarding table. The Layer 2 device forwards multicast packets based on the Layer 2 multicast forwarding table.
Run the mld-snooping enable command to enable MLD snooping on an AP's wired interface.
By default, MLD snooping is disabled on an AP's wired interface.
MLD snooping is a basic IPv6 Layer 2 multicast function that forwards and controls multicast traffic at the data link layer. MLD snooping runs on a Layer 2 device and analyzes MLD messages exchanged between a Layer 3 device and hosts to set up and maintain a Layer 2 multicast forwarding table. The Layer 2 device forwards multicast packets based on the Layer 2 multicast forwarding table.
Run the vlan { tagged | untagged } { vlan-id1 [ to vlan-id2 ] } &<1-10> command to configure the VLAN to which an AP's wired interface is added.
By default, an AP's wired interface allows packets from all VLANs to pass. The wired interface is added to VLAN 1 in untagged mode and to other VLANs in tagged mode.
An AP's wired interface directly connects to a host. Add the wired interface to a VLAN or a group of VLANs in untagged mode using the untagged parameter. After the wired interface is added to the VLAN, the interface removes VLAN tags of frames before sending frames to the host.
When an AP's wired interface connects to a Layer 2 network, add the wired interface to a VLAN or a group of VLANs in tagged or untagged mode based on the condition of peer devices using the tagged or untagged parameter, respectively.
Run the traffic-filter { inbound | outbound } { ipv4 | ipv6 | l2 } acl { acl-number | name acl-name } or traffic-filter { inbound | outbound } ipv4 acl { acl-number | name acl-name } l2 acl { acl-number | name acl-name } command to configure ACL-based packet filtering on an AP's wired interface.
By default, ACL-based IPv4, IPv6, or Layer 2 packet filtering is not configured on an AP's wired interface.
Before the traffic-remark command is run, an ACL rule must have been created.- acl (system view)
- acl ipv6 (system view)
- acl name
- acl ipv6 name
Run the traffic-remark { inbound | outbound } { ipv4 | ipv6 | l2 } acl { acl-number | name acl-name } { dot1p dot1p-value | dscp dscp-value }, or traffic-remark { inbound | outbound } ipv4 acl { acl-number | name acl-name } l2 acl { acl-number | name acl-name } { dot1p dot1p-value | dscp dscp-value } command to configure ACL-based priority re-marking on an AP's wired interface.
By default, ACL-based priority re-marking is not configured on an AP's wired interface.
Before the traffic-remark command is run, an ACL rule must have been created.- acl (system view)
- acl ipv6 (system view)
- acl name
- acl ipv6 name
Run the user-isolate { all | l2 } command to configure the user isolation function on an AP wired port profile.
By default, user isolation is disabled on an AP's wired interface.
The user isolation function prevents users on the same wired interface from communicating with each other. All user traffic on the wired interface is forwarded by the gateway. Therefore, this function ensures communication security on wired interfaces and allows uniform charging for users.
Precautions
Eth-Trunk member interfaces do not support the user isolation function.
Run the vlan pvid vlan-id command to configure a PVID for an AP's wired interface.
By default, no PVID is configured for an AP wired interface.
When receiving an untagged packet from a peer device, an AP's wired interface adds a VLAN tag to the packet. After the PVID is configured on the wired interface, the interface adds the PVID to all the received untagged packets.
Precautions
Eth-Trunk member interfaces do not support PVID setting.
The PVID can be configured in different modes for an AP's wired interface.- When the AP's wired interface works in root mode and has been configured to transmit packets carrying the management VLAN tag using the management-vlan vlan-id command, the PVID for the AP's wired interface must be configured the same as the management VLAN ID.
- When the AP's wired interface works in endpoint mode, the PVID can be directly configured.
- When the AP's wired interface works in middle mode, the PVID cannot be configured.
- Run quit
Return to the WLAN view.
- Configure link layer parameters for an AP's wired interface
- Bind the AP wired port profile to an AP group or AP.
- Bind the AP wired port profile to an AP group.
- Run the ap-group name group-name command to enter the AP group view.
Run the wired-port-profile profile-name interface-type interface-number command to bind the AP wired port profile to an AP group.
By default, the AP wired port profile default is bound to an AP group.
- Bind the AP wired port profile to to an AP.
- Run the ap-id ap-id, ap-mac ap-mac, or ap-name ap-name command to enter the AP view.
Run the wired-port-profile profile-name interface-type interface-number command to bind the AP wired port profile to an AP.
By default, no AP wired port profile is bound to an AP.
- Bind the AP wired port profile to an AP group.
Verifying the Configuration
- Run the display wired-port-profile { all | name profile-name } command to check configuration and reference information about an AP wired port profile.
- Run the display port-link-profile { all | name profile-name } command to check configuration and reference information about an AP wired port link profile.
- Run the display references wired-port-profile name profile-name command to check reference information about an AP wired port profile.
- Run the display references port-link-profile name profile-name command to check reference information about an AP wired port link profile.
- Run the display mac-address mac-address [ verbose ] ap-all command to check MAC address entries on all APs.
- Run the display mac-address { ap-id ap-id | ap-name ap-name } interface-type interface-number command to check all dynamic MAC address entries on an AP's wired interface.
- Run the display ap wired-port interface-type interface-number { ap-name ap-name | ap-id ap-id } command to display configuration of an AP's wired interface.