Configuration Roadmap
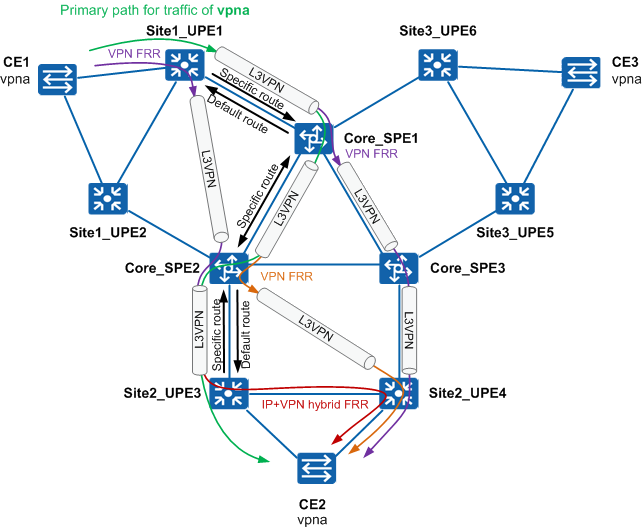
On a rail transmit bearer network, IP tunnels between nodes need to be enabled to bear L3VPN services. For example, set up a hierarchical L3VPN tunnel from Site1_UPE1 to Site2_UPE3 to transmit IP data services between Site1 and Site2, as shown in Figure 1.
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Deploy MP-BGP.
- Set up MP-IBGP peer relationships between UPEs and SPEs and between SPEs.
- Configure routing rules to enable traffic from UPEs to SPEs is forwarded through the default route and traffic from SPEs to UPEs is forwarded through specific routes.
- Configure route priority policies to enable UPEs to forward traffic to other sites preferentially through SPEs directly connected to the UPEs.
- Configure route priority policies to enable SPEs to forward traffic to other sites preferentially through UPEs directly connected to the SPEs.
- Configure route filtering policies to disable SPEs from advertising ARP Vlink direct routes at the local sites to UPEs at other sites.
- Configure route filtering policies to disable SPEs from receiving route information about sites directly connected to them from other SPEs, preventing route loops. For example, disable Core_SPE2 from receiving routes of Site1 from Core_SPE1 and routes of Site2 from Core_SPE3.
Deploy VPN services.
- Deploy VPN instances on UPEs and SPEs, and bind interfaces to the VPN instances on UPEs, but not on SPEs.
- Preferentially use TE tunnels to bear VPN services on UPEs. In hybrid FRR mode, LSP tunnels can be used to bear VPN services.
- Configure a tunnel policy selector on an SPE to enable the SPE to select any tunnel policy when the next-hop address of a VPNv4 route has the prefix of another SPE and to select a TE tunnel in other scenarios.
- Deploy VRRP on two UPEs at a site, and send information about ARP Vlink direct routes to the neighboring SPEs so that the SPEs select the optimal route to send packets to the CE.
Configure reliability protection.
- Deploy VRRP on two UPEs at a site to implement gateway backup and ensure reliability of uplink traffic on CEs. Configure backup devices to forward service traffic, minimizing the impact of VRRP switchovers on services.
- Deploy VPN FRR on a UPE. If the TE tunnel between the UPE and an SPE is faulty, traffic is automatically switched to the TE tunnel between the UPE and another SPE at the same site, minimizing the impact on VPN services.
- Deploy VPN FRR on an SPE, for example Core_SPE1. If Core_SPE2 connected to SPE1 is faulty, Core_SPE1 switches VPN services to Core_SPE3, implementing fast E2E switchovers of VPN services.
- Deploy VPN FRR on an SPE. If the TE tunnel between the SPE and a UPE is faulty, traffic is automatically switched to the TE tunnel between the SPE and another UPE at the same site, minimizing the impact on VPN services.
- Deploy IP+VPN hybrid FRR on UPEs. If the interface of a UPE detects a fault on the link between the UPE and its connected CE, the UPE quickly switches traffic to its peer UPE, and the peer UPE then forwards the traffic to the CE.
- Deploy VPN GR on all UPEs and SPEs to ensure uninterrupted VPN traffic forwarding during a master/backup switchover on the device transmitting VPN services.