BFD for OSPF
A link failure or topology change may lead to route recalculation. Therefore, the convergence time of routing protocols must be shortened as much as possible to improve network performance. A possible solution is to quickly detect link faults and immediately notify routing protocols of the faults.
BFD for OSPF associates a BFD session with OSPF. The BFD session quickly detects a link fault and notifies OSPF of the fault. OSPF quickly responds to the network topology change. Table 1 lists OSPF convergence time.
BFD Session |
Link Fault Detection Mechanism |
Convergence Time |
|---|---|---|
Not bound |
Timeout of the OSPF Hello keepalive timer |
At the second level |
Bound |
BFD session in Down state |
At the millisecond level |
Application
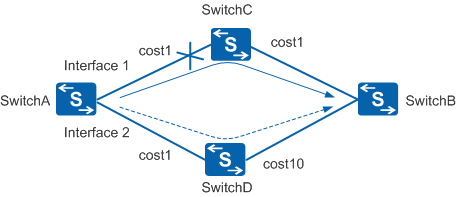
In Figure 1, SwitchA establishes OSPF neighbor relationships with SwitchC and SwitchD. The outbound interface in the route from SwitchA to SwitchB is Interface 1. Packets from SwitchA traverse SwitchC, and then reach SwitchB. When the OSPF neighbor is in Full state, the system instructs BFD to create a BFD session.
If a fault occurs on the link between SwitchA and SwitchC, the BFD session detects the fault and notifies SwitchA. SwitchA processes the neighbor Down event and recalculates the route. Interface 2 then becomes the new outbound interface in the route. Packets from SwitchA traverse SwitchD, and then reach SwitchB.