BFD for PIM
If a designated router (DR) on the shared network segment becomes faulty, Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) neighbor relationships time out. This triggers a new DR election among PIM neighbors, interrupting multicast data transmission. The interruption period, usually in seconds, is at least as long as the timeout interval of the neighbor relationship.
After detecting a fault on the peer, BFD immediately instructs the PIM module to trigger a new DR election without waiting for timeout of the neighbor relationship.
BFD for PIM can quickly detect faults on the Assert winner and is also applicable to Assert election on a shared network segment.
Table 1 lists the PIM convergence time.
BFD Session |
Link Fault Detection Mechanism |
Convergence Time |
|---|---|---|
Not bound |
Neighbor relationship timeout |
Second-level |
Bound |
BFD session in Down state |
Millisecond-level |
Application
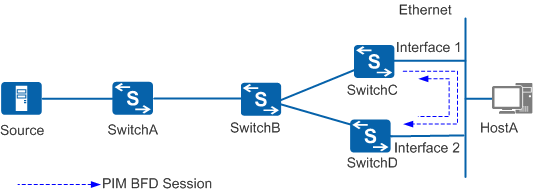
In Figure 1, on the shared network segment connected to user hosts, downstream interface Interface1 on SwitchC and downstream interface Interface2 on SwitchD establish a PIM BFD session and send BFD control packets to monitor the link status.
SwitchC functions as the DR and Interface1 is responsible for forwarding multicast data. If Interface1 becomes faulty, BFD fast notifies the RM of the session status and the RM notifies the PIM module. The PIM module then triggers a new DR election. SwitchD quickly begins functioning as the new DR and Interface2 begins forwarding multicast data to the receivers.