Defense Against Bogus DHCP Server Attacks
Mechanism
Because DHCP servers and DHCP clients lack authentication mechanisms between them, each DHCP server newly configured on a network assigns IP addresses and other network parameters to DHCP clients. If the assigned IP addresses and other network parameters are incorrect, errors may occur on the network.
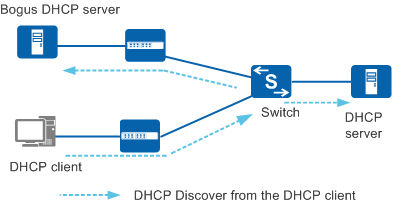
In Figure 1, authorized and unauthorized DHCP servers can receive DHCP Discover messages broadcast by DHCP clients.
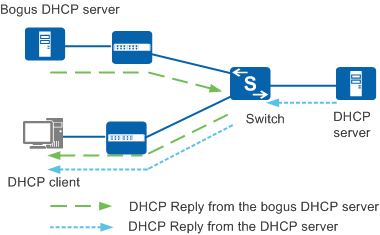
If a bogus DHCP server sends a bogus DHCP Reply message with an incorrect gateway address, Domain Name System (DNS) server address, or IP address to a DHCP client, as shown in Figure 2, the DHCP client cannot obtain the correct IP address and required information. The authorized user then fails to access the network and user information security is compromised.
Solution
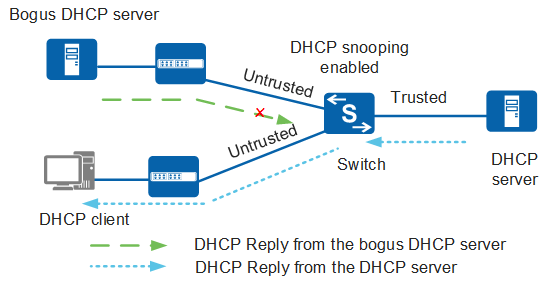
To prevent attacks from a bogus DHCP server, configure the trusted interface and untrusted interfaces on the device.
You can configure the interface directly or indirectly connected to the authorized DHCP server as the trusted interface and other interfaces as untrusted interfaces. The device then discards DHCP Reply messages received on untrusted interfaces, preventing bogus DHCP server attacks, as shown in Figure 3.