Defense Against DHCP Server DoS Attacks
Mechanism
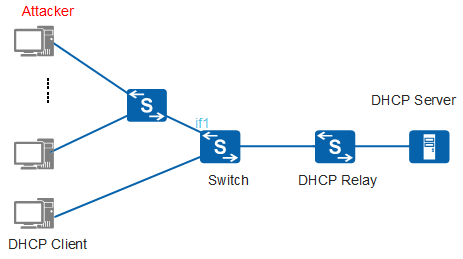
In Figure 1, if a large number of attackers request IP addresses on if1, IP addresses in the IP address pool are exhausted. This results in no IP addresses being available for authorized users.
A DHCP server identifies the MAC address of a client based on the client hardware address (CHADDR) field in the DHCP Request message. If an attacker continuously applies for IP addresses by changing the value of the CHADDR field, IP addresses in the address pool on the DHCP server may be exhausted. As a result, authorized users cannot obtain IP addresses.
Solution
To prevent DHCP server DoS attacks, enable DHCP snooping on the device and then set the maximum number of access DHCP clients allowed on the device or an interface. Only the allowed number of DHCP clients can obtain an IP address through the device or interface.
You can enable the device to check whether the MAC address in the Ethernet frame header matches the value of the CHADDR field in the DHCP message. If the two values match, the message is forwarded. Otherwise, the message is discarded.