DHCPv6 PD Implementation
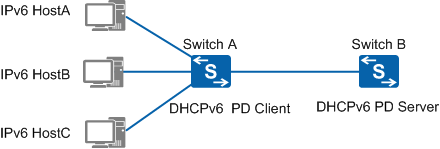
DHCPv6 prefix delegation (PD) is a prefix allocation mechanism and defined in RFC 3633. On a layered network, IPv6 addresses of different layers are configured manually. Manually configured IPv6 addresses have poor extensibility and cannot be planned and managed in a centralized manner.
The DHCPv6 PD mechanism allows a downstream device to request IPv6 prefixes from the upstream device and an upstream device to assign appropriate prefixes for the downstream device. In this way, you do not need to configure IPv6 prefixes for user-side links on the downstream device. The downstream device divides the obtained prefix (the length of the obtained prefix is smaller than 64 bits) into 64-bit prefix of subnet segments and sends a Route Advertisement (RA) packet on the link that IPv6 hosts directly connect to. This enables hosts to automatically configure addresses, completing IPv6 network deployment.
Figure 1 shows the working process of DHCPv6 PD.
The process of DHCPv6 PD using four-message exchange is as follows:
- A DHCPv6 PD client sends a Solicit packet, requesting an IPv6 address prefix from a DHCPv6 PD server.
- If the DHCPv6 PD server does not support fast address allocation, the DHCPv6 PD server returns an Advertise packet containing the allocated address prefixes regardless of whether the Solicit packet contains the Rapid Commit option.
- If receiving Advertise packets from multiple DHCPv6 PD servers, the DHCPv6 PD client selects the DHCPv6 PD server with the highest priority and sends a Request packet to this DHCPv6 PD server to request address prefixes.
- The DHCPv6 PD server responds with a Reply packet to assign an IPv6 address prefix to the DHCPv6 PD client.
DHCPv6 PD also supports two-message exchange using packets carrying the Rapid Commit option. For details, see DHCPv6 Two-Message Exchange