Fault Information Advertisement Between CFM and Other Modules
Fault Information Advertisement Between CFM and Detection Modules
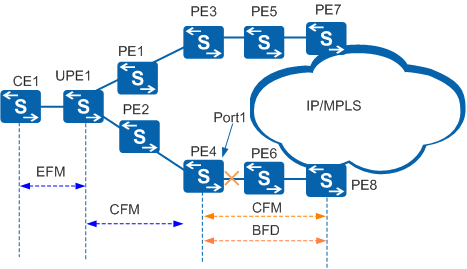
The OAMMGR module associates CFM with detection modules. The detection modules include EFM, BFD, and interface. Figure 1 shows a network on which fault information is advertised between CFM and detection modules.
Table 1 describes problems and solutions for fault information advertisement between CFM and detection modules over the path UPE1 -> PE2 -> PE4 -> PE6 -> PE8.
Function Deployment |
Problem |
Solution |
|---|---|---|
CFM is used to monitor the link between UPE1 and PE4. |
Although CFM detects a fault on the link between UPE1 and PE4, CFM cannot notify PE6 of the fault. As a result, network-side traffic is still sent to PE4, interrupting traffic. Although Port1 on PE4 goes Down, Port1 cannot notify CE1 of the fault. As a result, CE1 continues forwarding user traffic to PE4, interrupting traffic. |
Associate CFM with Port1:
The association between CFM and an interface is used to detect faults in an active link of a link aggregation group (LAG) in static LACP or 1:1 active/standby mode. If a fault is detected, a protection switchover is triggered. |
EFM is used to monitor the direct link between CE1 and UPE1. CFM is used to monitor the link between PE4 and UPE1. |
Although CFM detects a fault, CFM cannot notify CE1 of the fault. As a result, CE1 continues forwarding user traffic to PE4, interrupting traffic. |
Associate the EFM module with the CFM module:
|
CFM is configured to monitor links between UPE1 and PE4 and between PE4 and PE8. |
|
Associate both CFM modules with each other: If a CFM module detects a fault, it instructs the OAMMGR module to notify the other CFM module of the fault and sends an alarm to an NMS. A network administrator analyzes alarm information and takes measures to rectify the fault. |