Ethernet over GRE
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) provides a mechanism to encapsulate packets of a protocol into packets of another protocol. This allows packets to be transmitted over heterogeneous networks. A channel for transmitting heterogeneous packets is called a tunnel.
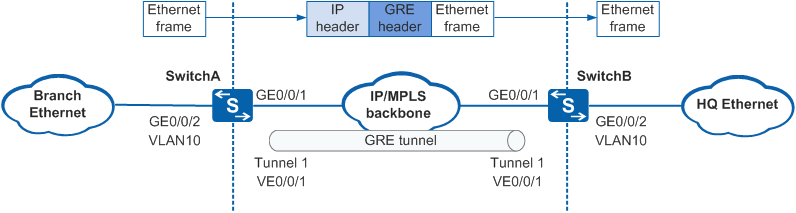
In Figure 1, the enterprise headquarters and branch use Ethernet networks and are connected by an IP/MPLS backbone network. Ethernet over GRE can be deployed to transparently transmit Ethernet packets over a GRE tunnel, enabling Layer 2 communication between the enterprise headquarters and branch.
Ethernet over GRE encapsulates Ethernet packets using GRE and transmits the encapsulated packets over a network running another network layer protocol, such as IPv4. The detailed working process is as follows:
- User-side physical Ethernet interface GE0/0/2 on SwitchA receives an Ethernet packet containing a VLAN tag from the branch network.
- SwitchA performs Layer 2 forwarding within the device based on the MAC address and VLAN tag and finds the outbound interface VE0/0/1.
- VE0/0/1 on SwitchA processes the Ethernet packet and forwards the packet to Tunnel 1 bound to it. Tunnel 1 encapsulates the Ethernet packet using GRE (with the protocol code 0x6558) and forwards the encapsulated packet to SwitchB over a GRE tunnel.
- Tunnel 1 on SwitchB decapsulates the received packet using GRE, finds that the protocol code is 0x6558, and forwards the decapsulated Ethernet packet to VE0/0/1 bound to Tunnel 1.
- After the decapsulated Ethernet packet reaches VE0/0/1 of SwitchB, SwitchB performs Layer 2 forwarding within the device based on the MAC address and VLAN, and finds the outbound interface GE0/0/2.
- SwitchB sends the Ethernet packet to the headquarters network through the outbound interface GE0/0/2.

As a Layer 2 tunnel, Ethernet over GRE can only forward unicast and broadcast packets of a specified VLAN but not multicast packets.