GRE Fundamentals
Implementation
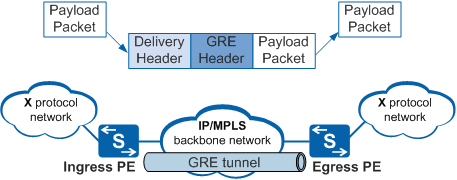
Packets transmitted over a GRE tunnel undergo encapsulation and decapsulation processes. An ingress provider edge (PE) device encapsulates packets of the X protocol and transmits them across a GRE tunnel, and the egress PE device decapsulates the packets. Figure 1 shows this process.
The packet encapsulation process is as follows:
The ingress PE receives an X protocol packet from the interface connected to the X network, and sends it to the X protocol.
The X protocol checks the destination address in the packet header and searches the routing table or the forwarding table for the outbound interface. If the outbound interface is a GRE tunnel interface, the ingress PE adds a GRE header to the packet.
Since the backbone network runs the IP protocol, the ingress PE adds an IP header to the packet. The source address and destination address in the IP header are the tunnel source and destination address, respectively.
The ingress PE searches the IP routing table for the outbound interface based on the destination address in the IP header (tunnel destination address) and transmits the packet over the IP backbone network.
For details on the format of the encapsulated packet, see Packet Format.
The decapsulation process is a reversal of the encapsulation process.
The egress PE receives the packet from the GRE tunnel interface and analyzes the IP header in the packet finding that the egress PE itself is the destination. The egress PE then removes the IP header and delivers the packet to the GRE protocol for processing.
The GRE protocol removes the GRE header and delivers the packet to the X protocol.
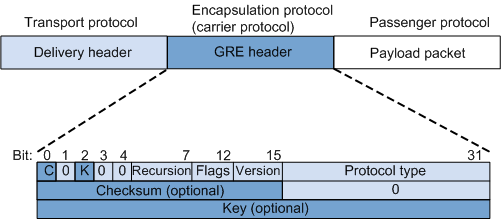
Packet Format
Passenger protocol: indicates the protocol of the original packet. The original packet is encapsulated in a GRE packet as the payload.
Encapsulation protocol (carrier protocol): indicates the protocol used to encapsulate passenger protocol packets by adding a GRE header.
Transport protocol (delivery protocol): indicates the protocol used to transmit encapsulated packets.
Table 1 describes the fields in a GRE header.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
C |
Checksum bit.
|
K |
Key bit.
|
Recursion |
Number of times a packet is encapsulated by GRE. The value of this field is incremented by 1 every time the packet is encapsulated. If the packet is encapsulated more than three times, the device discards the packet. This field prevents a packet from being encapsulated infinitely. NOTE:
|
Flags |
Reserved field. The value must be set to 0. |
Version |
Version number. The value must be set to 0. |
Protocol Type |
Passenger protocol type. A common passenger protocol is IPv4 protocol, with a value of 0800. |
Checksum |
Checksum of the GRE header and the payload. |
Key |
Keyword. This field is used to authenticate the packet at the receive end. |

Currently, the GRE header does not contain the Source Route field; therefore, bit 1, bit 3, and bit 4 are all set to 0.