HSB Implementation
HSB implementation involves data synchronization and traffic switching.
- Data synchronization is performed to ensure consistent information on the master and backup devices when the two devices are working normally.
- Traffic switching is performed to ensure non-stop service forwarding when the master device fails or recovers.
Data Synchronization
When the master device fails, service traffic can be switched to the backup device only if the backup device has the same session entries as the master device. If the session entries on the master and backup devices are different, sessions may be interrupted during traffic switching. Therefore, a mechanism is required to synchronize session information to the backup device when session entries are created or modified on the master device. The HSB service module provides data backup, sets up an HSB channel between the master and backup devices and maintains link status of the HSB channel. Session information is synchronized through the HSB channel.
Batch backup
During operation, the master device may save a large number of session entries. After a backup device is added to the network and HSB is configured on the two devices, the master device synchronizes all the session entries to the backup device at one time.
Real-time backup
When the master device generates new session entries or modifies existing session entries, it synchronizes new or modified session entries to the backup device in real time.
Traffic Switching
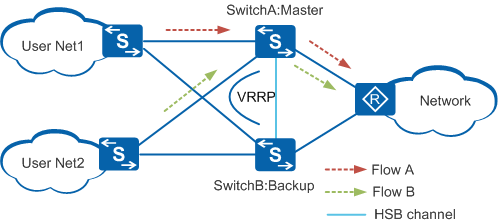
VRRP HSB implements traffic switching through VRRP.
As shown in Figure 1, VRRP is configured on SwitchA and SwitchB. In the VRRP group, SwitchA is the master device and SwitchB is the backup device. According to the VRRP status of the two routers, SwitchA becomes the master device in the HSB group, and SwitchB becomes the backup device. The HSB service synchronizes session information from SwitchA to SwitchB.
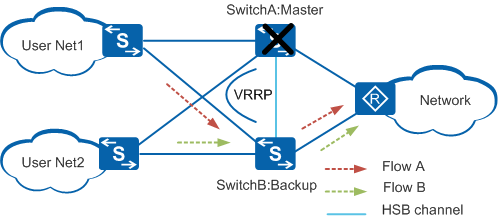
When SwitchA fails, as shown in Figure 2, the VRRP group selects a new master based on the VRRP priorities of the devices. SwitchB then becomes the master device, and service traffic is switched to SwitchB.