IGMPv1 Fundamentals
IGMPv1 Messages
- General Query: A querier sends General Query messages to all hosts and routers on the local network segment to discover which multicast groups have members on the network segment.
- Report: Hosts send Report messages to multicast routers to request to join a multicast group or respond to General Query messages.
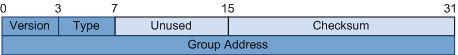
Figure 1 shows the IGMPv1 message format, and Table 1 describes the message fields.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Version | In IGMPv1 messages, this field is set to 1. |
| Type | The two message type options are:
|
| Unused | In IGMPv1 messages, this field is set to 0 by the sender and is ignored by the receiver. |
| Checksum | The checksum is 16 bits long. It is the one's complement of the one's complement sum of the whole IGMP message (the entire IP payload). When computing the checksum, a device initially sets the checksum field to 0. The sender computes the checksum and inserts it into this field. The receiver verifies the checksum before processing the message. |
| Group Address | In a General Query message, this field is set to 0. In a Membership Report message, this field is set to the address of the group that the member requests to join. |
How IGMPv1 Works
IGMPv1 uses a query-report mechanism to manage multicast groups. When there are multiple multicast routers on a network segment, all multicast routers can receive Membership Report messages from hosts. Therefore, only one multicast router needs to send Query messages to the network segment. The router selected to send Query messages is regarded as the IGMP querier. In IGMPv1 implementation, a unique Assert winner or designated router (DR) is selected by Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) as the querier. The querier is the only device that sends Host Membership Query messages on the local network segment.
For details about Assert and DR election, see PIM-DM and PIM-SM (ASM Model).
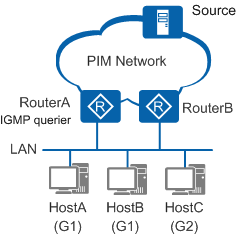
Figure 2 shows a network running IGMPv1. RouterA and RouterB connect to a network segment with three receivers: HostA, HostB, and HostC. RouterA is the IGMP querier on the network segment. HostA and HostB want to receive data sent to group G1, and HostC wants to receive data sent to group G2.
IGMPv1 involves three mechanisms: general query and report mechanism, join mechanism, and leave mechanism.
General query and report mechanism
By sending General Query messages and receiving Report messages, an IGMP querier knows which groups have members on the local network segment.
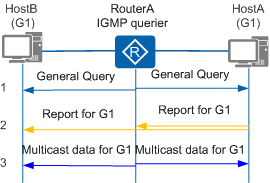
Figure 3 shows the general query and report process:
The IGMP querier sends a General Query message, with destination address 224.0.0.1 (indicating all hosts and routers on the network segment). All group members start a timer when they receive the General Query message.
The IGMP querier sends General Query messages at intervals. The interval is configurable and defaults to 60 seconds. HostA and HostB are members of G1 and start a timer for G1 (Timer-G1). The timer length is a random value between 0 and the maximum response time (10 seconds by default).
The host whose timer expires first sends a Report message for the group.
In this example, Timer-G1 on HostA expires first, and HostA sends a Report message with the destination address G1. When HostB receives the Report message sent by HostA, it stops Timer-G1 and does not send a Report message for G1. This mechanism reduces the number of Report messages transmitted on the network segment, lowering loads on multicast routers.
- After the IGMP querier receives the Report message from HostA, it knows that group G1 has members on the local network segment. The IGMP querier uses the multicast routing protocol to create a (*, G1) entry, in which * stands for any multicast source. Once the IGMP querier receives data sent to G1, it forwards the data to this network segment.
Join mechanism
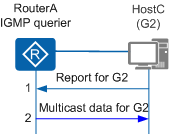
Figure 4 shows how HostC joins group G2:
- HostC sends a Report message for G2 without waiting for a General Query message.
- After receiving the Report message, the IGMP querier knows that a member of G2 has connected to the local network segment, and creates a (*, G2) entry. Once the IGMP querier receives data sent to G2, it forwards the data to this network segment.
Leave mechanism
IGMPv1 does not define a Leave message. After a host leaves a group, it no longer responds to General Query messages. On the network in Figure 2:
If HostA leaves group G1
When HostA receives General Query messages from the IGMP querier, it does not send a Report message for G1. Group G1 has another member HostB on the network segment, which still sends Report messages for G1 in response to General Query messages. Therefore, the IGMP querier is unaware HostA has left the group.
If HostC leaves group G2
When HostC receives General Query messages from the IGMP querier, it does not send a Report message for G2. Because G2 has no other members on this network segment, the IGMP querier no longer receives Report messages for G2. After a certain period (130 seconds by default), the IGMP querier deletes the (*, G2) entry.