Overview of IGMP Snooping
Definition
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping is a Layer 2 IPv4 multicast protocol. It listens to multicast protocol packets exchanged between the upstream Layer 3 multicast device and downstream hosts to maintain outbound interfaces of multicast packets. Based on the outbound interface information, IGMP snooping manages and controls the multicast forwarding at the data link layer.
Purpose
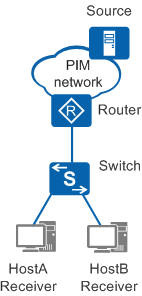
In most cases, especially in a LAN, multicast packets must pass through Layer 2 devices. In Figure 1, multicast packets must pass through a Layer 2 switch between multicast users and the router (Layer 3 multicast device).
After receiving multicast packets from the router, the switch forwards the multicast packets to the receivers. The destination address of multicast packets is a multicast group address. The switch cannot learn multicast MAC addresses, so it broadcasts multicast packets in the broadcast domain. All hosts in the broadcast domain will receive the multicast packets, regardless of whether they are members of the multicast group. This wastes network bandwidth and threatens network security.
IGMP snooping solves this problem. With IGMP snooping enabled, a Layer 2 multicast device can listen to and analyze IGMP messages between multicast users and the upstream router. The Layer 2 multicast device sets up Layer 2 multicast forwarding entries to control multicast data forwarding. In this way, multicast data is not broadcast on the Layer 2 network.