Understanding mDNS Relay
Service Provisioning Device Advertises Services to the mDNS Gateway
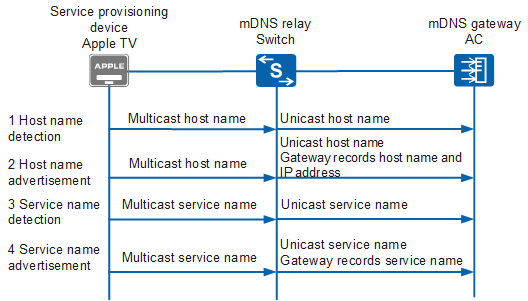
Each service provisioning device advertises available services to an mDNS gateway, so the mDNS gateway can record information about all available services. A host name identifies a service provisioning device. A service name identifies a service provided by service provisioning device and records the service type. For example, the service name Officejet Pro 8100 [C12FFA] (7)._printer._tcp.local indicates that the service provisioning device can provide the printing service. Each service provisioning device can provide various services. Figure 1 shows how a service provisioning device advertises services to the mDNS gateway.
Detect host name
- After the Apple TV supporting Bonjour is powered on, it generates a host name and sends an mDNS request packet with the destination multicast address of 224.0.0.251 to check whether the host name is unique.
- After receiving an mDNS request packet, the mDNS relay changes the destination multicast address to the IP address of the specified mDNS gateway and unicasts an mDNS request packet to the mDNS gateway.
After receiving the mDNS request packet, the mDNS gateway queries its recorded host name lists.
If the host name already exists, it is used by another service provisioning device. The mDNS gateway sends a response packet indicating the host name conflict to the mDNS relay. After receiving the response packet, the mDNS relay changes the destination address into the multicast address and multicasts the packets in its VLAN. After receiving the response packet indicating the host name conflict, the Apple TV regenerates another host name and sends an mDNS request packet again to check whether the host name is unique. If the Apple TV does not receive the response packet from the mDNS gateway within the detection period, the host name is unique.
Advertise host name
The Apple TV multicasts an mDNS request packet to advertise its host name and IP address. After receiving an mDNS request packet, the mDNS relay changes the destination multicast address to the IP address of the specified mDNS gateway and unicasts an mDNS request packet to the mDNS gateway. After receiving the mDNS request packet, the mDNS gateway records the host name and IP address of the Apple TV.
Detect service name
- The Apple TV sends an mDNS request packet with the destination multicast address of 224.0.0.251 to check whether the service name is unique.
- After receiving an mDNS request packet, the mDNS relay changes the destination multicast address to the IP address of the specified mDNS gateway and unicasts an mDNS request packet to the mDNS gateway.
After receiving the mDNS request packet, the mDNS gateway queries its recorded service lists.
If the service name already exists, it is used by another service provisioning device. The mDNS gateway sends a response packet indicating the service name conflict to the mDNS relay. After receiving the response packet, the mDNS relay changes the destination unicast address into the multicast address and multicasts the packets in its VLAN. After receiving the response packet indicating the service name conflict, the Apple TV regenerates another service name and sends an mDNS request packet again to check whether the service name is unique. If the Apple TV does not receive the response packet from the mDNS gateway within the detection period, the service name is unique.
The Apple TV multicasts an mDNS packet to advertise its service information. After receiving an mDNS request packet, the mDNS relay changes the destination multicast address to the IP address of the specified mDNS gateway and unicasts an mDNS request packet to the mDNS gateway. After receiving the mDNS request packet, the mDNS gateway records the service information, including the service name, service type, and TTL.
The TTL is provided by a service provisioning device to the mDNS gateway. The TTL in a service list recorded on the mDNS gateway indicates the aging time of a service. If the mDNS gateway receives mDNS request packets from a service provisioning device within the aging time, the mDNS gateway updates its service information. If the mDNS gateway does not receive mDNS request packets from a service provisioning device within the aging time, the mDNS gateway deletes its service information.
Bonjour-compatible Terminal Discovers Services
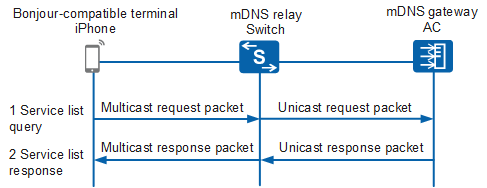
A Bonjour-compatible terminal (iPhone) multicasts an mDNS request packet to query required services. After receiving an mDNS request packet, the mDNS relay changes the destination multicast address to the IP address of the specified mDNS gateway and unicasts an mDNS request packet to the mDNS gateway.
After receiving the mDNS request packet, the mDNS gateway searches its service lists and unicasts the host name and IP address of the device that can provide the required service to the mDNS Relay. After receiving a response packet, the mDNS relay changes the destination address into the multicast address and multicasts the response packet in its VLAN. The Bonjour-compatible terminal that receives the response packet can establish a connection with a service provisioning device.
mDNS Relay Periodically Discovers Services
The mDNS relay periodically multicasts an mDNS request packet to discover services. The mDNS relay periodically multicasts an mDNS request packet to detect services in its VLAN. After receiving the mDNS request packet, service provisioning devices send response packets. The mDNS relay then forwards service information to the mDNS gateway. The mDNS gateway updates its service lists after receiving the response packets. With the periodic service discovery function, service provisioning devices can immediately advertise service information to the mDNS gateway, and the mDNS gateway can maintain integrity of its service lists in a timely manner.