Application Scenarios for mDNS Gateways
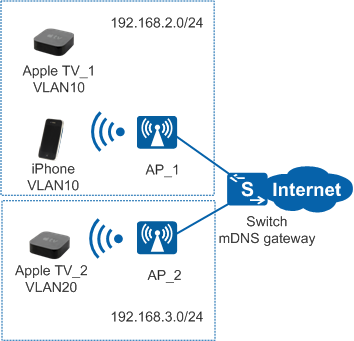
As shown in Figure 1, an enterprise provides wireless networks, Apple TV_1, and Apple TV_2 are located in different VLANs. Layer 2 forwarding is performed between the Switch and AP_1 and AP_2. Apple TV_1 in VLAN 10, and Apple TV_2 in VLAN 20 are all Bonjour-compatible terminals. Bonjour uses the multicast address 224.0.0.251 as the destination address, which is only valid within a Layer 2 broadcast domain, so Bonjour-compatible terminals can only provide services in their VLANs.
The mDNS gateway is deployed on the Switch so that the Bonjour-compatible terminal in VLAN 10 can discover services in VLAN 20. The mDNS gateway records service lists in VLAN 10 and VLAN 20, and responds to service requests from Bonjour-compatible terminals.

If the device is configured as an AC and communicates with APs at Layer 3, and the direct forwarding mode is configured on APs, mDNS packets cannot be encapsulated and sent to the AC through a CAPWAP tunnel.
When deploying mDNS gateway services, it is recommended that you configure the mDNS group function and the service types that can be recorded by the mDNS gateway.
An mDNS gateway can be configured to record airplay and printer services (a maximum of 64 airplay and printer devices are allowed), meeting the requirements in high-density WLANs and enterprise office WLANs as well as the requirements in manufacturing, finance, and government sectors.
An mDNS gateway can be configured to record airplay and printer services (a maximum of 256 airplay and printer devices are allowed), meeting the requirements in scenarios where the number of VLANs to which concurrent users belong is less than 36.