MLD SSM Mapping
Source-Specific Multicast (SSM) requires multicast routers to know multicast sources that hosts specify when they join a multicast group. A host running MLDv2 can specify multicast source addresses in MLDv2 Report messages. Some hosts can run only MLDv1. To enable such hosts to obtain the SSM service, multicast routers need to provide the MLD SSM mapping function.
MLD SSM mapping is implemented based on static SSM mapping entries. A multicast router converts (*, G) information in MLDv1 Multicast Listener Report messages to (G, INCLUDE, (S1, S2...)) information according to static SSM mapping entries to provide the SSM service for MLDv1 hosts.
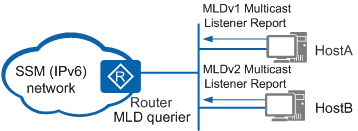
On the IPv6 SSM network shown in Figure 1, HostA runs MLDv1, while HostB runs MLDv2. If the MLD version of HostA cannot be upgraded to MLDv2, configure MLD SSM mapping on the router.
- If G is out of the IPv6 SSM group address range, the router provides the ASM service.
- If G is within the IPv6 SSM group address range:
- If the router has no MLD SSM mapping entry matching G, it does not provide the SSM service and drops the Report message.
- If the router has an MLD SSM mapping entry matching G, it converts (*, G) information in the Report message into (G, INCLUDE, (S1, S2...)) information and provides the SSM service for the hosts.

MLD SSM Mapping does not apply to MLDv2 Multicast Listener Report messages. To enable hosts running any MLD version on a network segment to obtain the SSM service, MLDv2 must run on interfaces of multicast routers on the network segment.