LDP Session Setup
LSRs use LDP discovery mechanisms to discover LDP peers and establish an LDP session. An LDP LSP can be established to transmit services only after LDP sessions are established.
LDP Discovery Mechanisms
LSRs use LDP discovery mechanisms to discover LDP peers. LSRs can use the following types of LDP discovery mechanisms:
Basic discovery mechanism: discovers directly-connected LSR peers on links.
LSRs periodically send LDP Link Hello messages through the basic discovery mechanism to establish local LDP sessions.
LDP Link Hello messages are encapsulated in UDP packets with the multicast destination address 224.0.0.2. If an LSR receives an LDP Link Hello message on an interface, the LSR connects to an LDP peer through this interface.
Extended discovery mechanism: discovers LSR peers not directly connected on links.
LSRs periodically send LDP Targeted Hello messages to specified destination IP addresses to establish remote LDP sessions through the extended discovery mechanism.
LDP Targeted Hello messages are encapsulated in UDP packets with unicast destination IP addresses. If an LSR receives LDP Targeted Hello messages, LDP peers are connected to this LSR.
LDP Session Setup Process
Two LSRs exchange Hello messages to establish an LDP session.
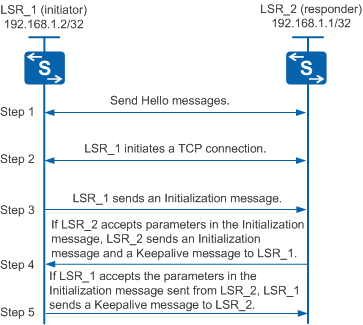
Figure 1 shows the process of establishing an LDP session.
The LDP session setup process is as follows:
Two LSRs send Hello messages to each other.
Each Hello message contains the transport address (device IP address) used to establish an LDP session.
The LSR with a larger transport address initiates a TCP connection.
LSR_1 initiates a TCP connection and LSR_2 waits for the TCP connection request, as shown in Figure 1.
After the TCP connection is successfully established, LSR_1 sends an Initialization message to negotiate parameters with LSR_2 to establish the LDP session.
These parameters include the LDP version, label distribution mode, Keepalive timer value, maximum packet data unit (PDU) length, and label space.
If LSR_2 accepts the parameters in the Initialization message, LSR_2 sends an Initialization message and a Keepalive message to LSR_1.
If LSR_2 rejects the parameters in the Initialization message, LSR_2 sends a Notification message to LSR_1 to stop the establishment process.
Parameters in the Initialization message include the LDP version, label distribution mode, Keepalive timer value, maximum PDU length, and label space.
If LSR_1 accepts the parameters in the Initialization message, LSR_1 sends a Keepalive message to LSR_2.
If LSR_1 rejects the parameters in the Initialization message, LSR_1 sends a Notification message to LSR_2 to stop the establishment process.
After both LSR_1 and LSR_2 have accepted Keepalive messages from each other, an LDP session is established between them.