RSVP GR
RSVP Graceful Restart (GR) ensures uninterrupted traffic transmission on the forwarding plane when traffic is switched to the control plane upon a node failure.
Background
Concepts
RSVP GR is a fast state recovery mechanism for RSVP-TE. As one of the high-reliability technologies, RSVP GR is designed based on non-stop forwarding (NSF).
The GR process involves GR restarter and GR helper routers. The GR restarter restarts the protocol and the GR helper assists in the process.
- Hello message with GR extensions: is used to detect the neighbor's GR status.
- GR Path message: is sent downstream and carries information about the last Path update.
- Recovery Path message: is sent upstream and carries information about the last received Path message.
Implementation
RSVP GR detects the GR status of a neighbor using RSVP Hello extensions.
RSVP GR is implemented as follows:
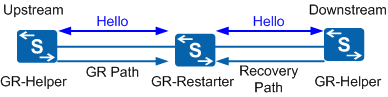
In Figure 2, after the GR restarter triggers a GR, it stops sending Hello messages to its neighbors. If a GR helper does not receive Hello messages for three consecutive intervals, it considers that the neighbor is performing a GR and retains all forwarding information. Meanwhile, the device continues to transmit services and wait for the GR restarter to complete the process.
After the GR restarter starts, it receives Hello messages from neighbors and sends Hello messages in response. Upstream and downstream nodes process Hello messages in different ways:
When the upstream GR helper receives a Hello message, it sends a GR Path message downstream to the GR restarter.
When the downstream GR helper receives a Hello message, it sends a Recovery Path message upstream to the GR restarter.
When receiving the GR Path message and the Recovery Path message, the GR restarter reestablishes the path state block (PSB) and reservation state block (RSB) of the CR-LSP based on the two messages. Information about the CR-LSP on the local control plane is restored.
If the downstream GR helper cannot send Recovery Path messages, the GR restarter reestablishes the local PSB and RSB using only GR Path messages.
Usage Scenario
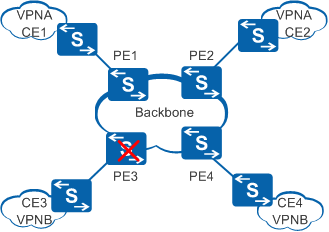
RSVP GR can be deployed to improve device-level reliability for nodes when an MPLS TE tunnel is set up using RSVP TE.
Benefits
When an active/standby switchover occurs on the control plane, RSVP GR ensures uninterrupted data transmission, improving device-level reliability.