Multicast Ping and Multicast Tracert
Introduction to Multicast Ping and Multicast Tracert
As the Internet develops, more and more data, voice, and video service information is exchanged across networks, and multicast services are rapidly developing to meet this need. Multicast ping (MPing) and multicast tracert (MTrace) have been developed to provide users with the multicast service detection and fault diagnosis functions. They are described as follows:
- MPing: a tool for detecting multicast services. MPing sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages to trigger the setup of the multicast distribution tree and detect members of reserved multicast groups on the network.

Reserved multicast group addresses range from 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255. For example, 224.0.0.5 is reserved for the OSPF multicast group, and 224.0.0.13 is reserved for the PIM multicast group.
- MTrace: a tool for tracing multicast forwarding paths. MTrace traces the path from a receiver to a multicast source along the multicast distribution tree.
MPing
MPing uses standard ICMP messages to detect the connectivity of a multicast path. MPing constructs an ICMP Echo Request message with the encapsulated destination address being a multicast address (either a multicast address for the reserved multicast group or a common multicast group address).
- If the encapsulated destination address of an ICMP Echo Request message is the address of a reserved multicast group, the querier must specify the outbound interface of the message. Upon receiving such an ICMP Echo Request message, the member of the reserved multicast group responds with an ICMP Echo Reply packet. Therefore, you can ping the address of the reserved multicast group to detect the members in the reserved multicast group.
- If the encapsulated destination address of an ICMP Echo Request message is the address of a common multicast group, the querier cannot specify the outbound interface of the message. The ICMP Echo Request message is forwarded on the multicast network, which triggers the setup of multicast routing entries. The querier collects statistics on ICMP Echo Reply packets received from the destination host and calculates the TTL and response time from the multicast source to a group member.
MTrace
MTrace complies with the protocol draft draft-fenner-traceroute-ipm-01.txt defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
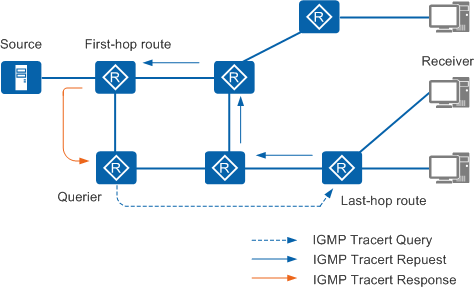
This draft describes a mechanism to trace the path along which multicast data is forwarded from the multicast source to the designated receiver. Figure 1 shows message exchanges in an MTrace process.
MTrace takes effect only on a network where a multicast protocol (such as PIM-SM) is enabled and the multicast distribution tree is established. MTrace detects the multicast forwarding path by sending query messages. Query messages include IGMP Tracert Query messages, IGMP Tracert Request messages, and IGMP Tracert Response messages.
MTrace is implemented as follows:
The querier sends an IGMP Tracert Query message to the last-hop device connected to the destination host.
After receiving the IGMP Tracert Query message, the last-hop device adds a response data block containing information about the interface that received the IGMP Tracert Query message, and sends an IGMP Tracert Request message to the previous-hop device.
Devices of each hop add a response data block to the IGMP Tracert Request message and send the message upstream.
When the first-hop device connected to the multicast source receives the IGMP Tracert Request message, it adds a response data block and sends the IGMP Tracert Response message to the querier.
The querier analyzes the IGMP Tracert Response message and obtains information about the forwarding path from the multicast source to the destination host.
If the IGMP Tracert Request message cannot reach the first-hop device due to an error, the IGMP Tracert Response message is directly sent to the querier. The querier then analyzes the data block information for locating and monitoring the faulty node.