MSDP-based Anycast RP
RPs set up MSDP peer relationships to exchange SA messages, so that locally registered source information can be shared by the RPs. Anycast RP is an application of this feature in one PIM-SM domain.
In a traditional PIM-SM domain, each group maps to one RP. When the network is overloaded or heavy traffic is transmitted within a short time, many network problems occur, such as the heavy load on the RP, slow network convergence after the RP fails, and multicast traffic forwarding over non-optimal paths. Anycast RP allows multiple RPs in a PIM-SM domain to use the same IP address and set up MSDP peer relationships. This feature enables multicast traffic to be forwarded over optimal paths and load balanced.
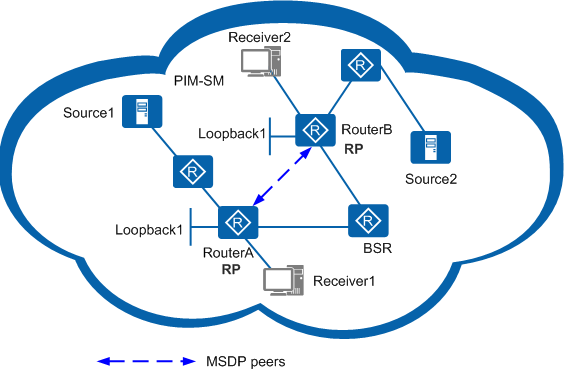
In the PIM-SM domain shown in Figure 1, multicast sources Source1 and Source2 send multicast data to group G. Receiver1 and Receiver2 are members of group G.
Perform the following configuration to apply Anycast RP in the PIM-SM domain:
- Select several routers that can act as RPs in the PIM-SM domain, such as RouterA and RouterB in Figure 1.
- Choose one loopback interface from each router, such as Loopback1, and assign the same address to these interfaces.
- Configure RPs. You can configure a static RP or configure C-RPs
for dynamic RP election:
- Static RP: Configure a static RP address (address of Loopback1 on RouterA) on all PIM-SM routers.
- C-RP: Configure the two Loopback1 interfaces on RouterA and RouterB as C-RPs. Configure a C-BSR on the network. Ensure that the C-RP addresses are different from the C-BSR address.
- Set up an MSDP peer relationship between RouterA and RouterB. Do not set up the MSDP peer relationship with the interface address used the RP address.
- Optimal path between RPs: A multicast source registers to the closest RP to set up an optimal SPT. Receivers send Join messages to the closest RP to set up an optimal RPT.
- Load balancing between RPs: Each RP only needs to maintain information about some of sources and groups in the PIM-SM domain, and forward some multicast packets.
- RP redundancy: When an RP fails, the multicast sources and receivers registered to this RP choose another closest RP to register and join.