Application Scenarios for Multicast VPN
Multicast VPN isolates multicast services of different VPN instances in an autonomous system (AS).
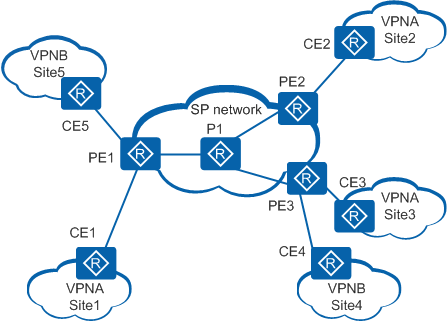
Figure 1 shows a BGP/MPLS IP VPN network with a single AS. On the network, PE1, PE2, and PE3 are configured with two VPN instances: VPNA and VPNB. Each VPN instance has the same Share-Group address and joins the same MD on the PE devices. After a Share-MDT is established, protocol and data packets from the VPNs can be transmitted through corresponding multicast tunnels (MTs).
To implement VPN multicast services in an AS, perform the following configurations:
- Configure reachable routes and run MPLS on the public network. Run routing protocols between PE and CE devices, and establish BGP peer relationships between PE devices to transmit VPN route information.
- Enable IP multicast routing for the public network instance and VPN instances on PE devices. Enable PIM-DM or PIM-SM on all interfaces connected to the public network and VPN sites. If PIM-SM is enabled, select appropriate candidate bootstrap routers (C-BSRs), candidate rendezvous points (C-RPs), or a static RP on the public network.
- Enable IGMP on PE and CE interfaces connected to VPN sites with receivers.
- Enable IP multicast routing on devices at each site. Enable PIM-DM or PIM-SM on all interfaces of the devices. If PIM-SM is enabled, select appropriate C-BSRs, C-RPs, or a static RP at the site.
- Configure different Share-Group addresses and Switch-Group-Pool ranges for VPNA and VPNB.