DNS Test
The NQA DNS test is performed using the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets. The NQA client simulates a DNS client and sends a DNS request to a specified Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server. This test helps you determine DNS server availability and measure DNS resolution speed.
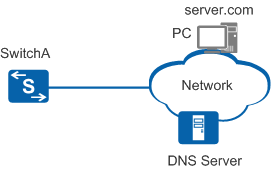
Figure 1 shows the process of a DNS test:
The DNS client (SwitchA) sends a DNS query packet to the DNS server, requesting the server to resolve a specified DNS name.
The DNS server receives the query packet, constructs a response packet, and sends it to the client.
SwitchA receives the response packet and calculates the time between when it sent the query packet and when it received the response packet.
A DNS test only simulates the DNS resolution process. It does not save the mapping between domain names and IP addresses.
However, DNS test results and historical records are collected in test instances. You can run commands to view the test results and historical records.