Concepts
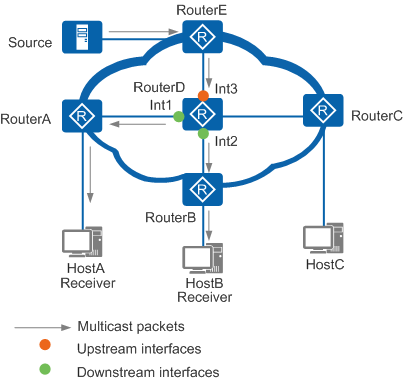
Concepts in this section are described with reference to the network shown in Figure 1.
Multicast Distribution Tree
On a PIM network, a point-to-multipoint (P2MP) multicast forwarding path is established for each multicast group. The multicast forwarding path is also called a multicast distribution tree (MDT) because of its tree shape.
Two types of MDT are available:
Shortest path tree (SPT) uses the multicast source as the root and multicast group members as leaves. SPT applies to both PIM-DM and PIM-SM networks.
In Figure 1, the MDT, RouterE → RouterD → RouterA/RouterB, is an SPT, on which the source is the root and HostA and HostB are leaves.
Rendezvous point tree (RPT) uses a rendezvous point (RP) as the root and multicast group members as leaves. RPT applies to PIM-SM networks.
For details about RP and RPT, see PIM-SM (ASM Model).
PIM Router
Routers with PIM enabled on interfaces are called PIM routers. Roles of routers on an MDT include:
Leaf router
A router that connects to user hosts, which may not be multicast group members. RouterA, RouterB, and RouterC in Figure 1 are leaf routers.
First-hop router
A router that directly connects to the multicast source on the multicast forwarding path and is responsible for forwarding multicast data from the multicast source. RouterE in Figure 1 is the first-hop router.
Last-hop router
A router that directly connects to multicast group members (receivers) on the multicast forwarding path and is responsible for forwarding multicast data to these members. RouterA and RouterB in Figure 1 are last-hop routers.
Intermediate router
A router located between the first-hop and last-hop routers. RouterD in Figure 1 is an intermediate router.
PIM Routing Entry
A PIM routing table contains two types of PIM routing entries: (S, G) and (*, G), where S indicates a specific multicast source, G indicates a specific multicast group, and * indicates any multicast source.
- (S, G) entries are typically used to establish an SPT on a PIM-DM or PIM-SM network.
- (*, G) entries are typically used to establish an RPT on a PIM-SM network.
A PIM router may have both (S, G) and (*, G) entries. When a PIM router receives a multicast packet with source address S and group address G and the packet passes the RPF check, the router forwards the packet according to the following rules:
- If a matching (S, G) entry exists, the router forwards the packet according to the (S, G) entry.
- If no matching (S, G) entry exists but a matching (*, G) entry exists, the router creates an (S, G) entry based on the (*, G) entry, and forwards the packet according to the (S, G) entry.
PIM routing entries contain the following information to guide multicast packet forwarding: