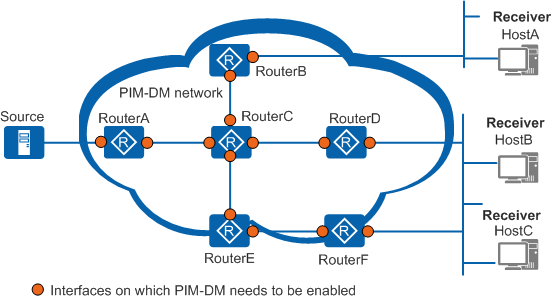
PIM-DM Application in a Single AS
Figure 1 shows multicast services deployed on a small-scale network. The Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) is running on the network and all network segments are reachable. Multicast group members are densely distributed. Hosts on this network want to receive video on demand (VoD) information, and network bandwidth needs to be used efficiently.
Implementation Plan
HostA, HostB, and HostC are receivers of multicast video streams. The entire PIM domain runs PIM-DM. RouterA connects to the multicast source. RouterB connects to the network segment of HostA. RouterD and RouterF connect to the network segment of HostB and HostC.
The network deployment must meet the following requirements:
PIM-DM must be enabled on all router interfaces.
IGMP must run between the routers and hosts on a shared network segment (between RouterB and HostA, and between RouterD/RouterF and HostB/HostC).
All router interfaces on the same network segment must run the same IGMP protocol version (IGMPv2 is recommended) and be configured with the same parameter settings, such as the query interval and timeout period of group memberships. If IGMP versions or parameter settings are inconsistent, IGMP group memberships on routers will be different.
After the network is deployed, HostA, HostB, and HostC can receive multicast data from the multicast source, and users can watch video programs they request.

To improve the stability of multicast services, statically add edge interfaces to multicast groups requested by users.