Overview of Portal Authentication
Definition
Portal authentication, also known as web authentication, authenticates end users on host systems that do not run an IEEE 802.1X client. Portal authentication websites are typically referred to as Portal websites. When a user accesses the Internet, the user must be first authenticated on the Portal website. If the authentication fails, the user can access only certain network resources. After the authentication succeeds, the user can access more network resources.
Benefits
- Ease of use: In most cases, Portal authentication directly authenticates a user on a web page, without any additional software required on the terminal.
- Convenient operations: Portal authentication allows for value-added services on the Portal page, including advertisement push and enterprise publicity.
- Mature technology: Portal authentication has been widely used in networks of carriers, fast food chains, hotels, and schools.
- Flexible deployment: Portal authentication implements access control at the access layer or at the ingress of key data.
- Flexible user management: Portal authentication can be performed on users based on the combination of user names and any one of VLANs, IP addresses, and MAC addresses.
Device Roles
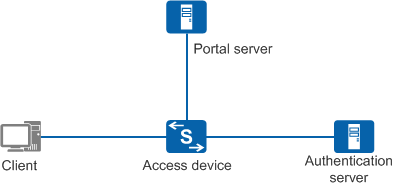
The Portal authentication system primarily consists of four components: client, access device, Portal server, and authentication server, as shown in Figure 1.
- Client: a host that has a browser running Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) installed.
- Access device: a switch or router, which provides the following functions:
- Redirects all HTTP or HTTPS requests of users on authentication subnets to the Portal server before authentication.
- Interacts with the Portal server and authentication server to implement user identity authentication, authorization, and accounting during authentication.
- Grants users access to specified network resources after successful authentication.
- Portal server: a server system that receives authentication requests from clients, provides free Portal services and authentication pages, and exchanges client authentication information with an access device.
- Authentication server: interacts with the access device to implement user authentication, authorization, and accounting.

A Portal server can be an external Portal server or a built-in Portal server integrated into an access device. The access device with a built-in Portal server implements basic Portal server functions, including web-based login and logout, and improves flexibility of Portal authentication. However, it cannot completely replace an independent Portal server, and does not support extended functions of an external Portal server, such as MAC address-prioritized Portal authentication.
Due to limited storage space, functions, and performance of access devices, the built-in Portal server applies to scenarios requiring simple functions and having a smaller number of access users, for example, small restaurants that provide Internet access services.