Portal Authentication Process Based on the Portal Protocol
This section describes the Layer 2 authentication process of an external Portal server. The authentication process of a built-in Portal server is similar to that of an external Portal server.
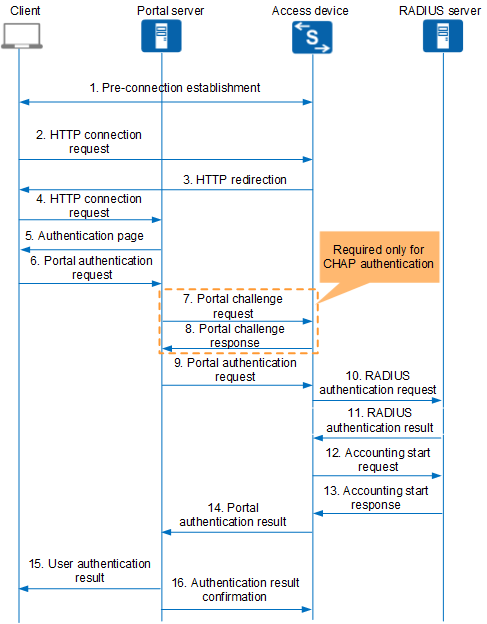
Figure 1 shows the packet exchange in the Layer 2 Portal authentication process based on the Portal protocol. The Layer 3 Portal authentication process is the same as the Layer 2 Portal authentication process, except that no pre-connection is established between the client and access device.
The authentication process is described as follows:
Before authentication, the client establishes a pre-connection with the access device. The access device creates a user online entry for the client and grants the client access to certain network resources.
The client initiates an HTTP connection request.
Upon receipt of the HTTP connection request packet, the access device determines whether to permit the packet. If the HTTP packet is destined for the Portal server or a publicly available network resource, the access device permits the packet. If the HTTP packet is destined for other addresses, the access device sends the URL of the Portal authentication page to the client.
The client sends an HTTP connection request to the Portal server based on the obtained URL.
The Portal server returns the Portal authentication page to the client.
- The user enters the user name and password on the Portal authentication page. The client then sends a Portal authentication request to the Portal server.
- (Optional) The Portal server sends a Portal challenge request packet (REQ_CHALLENGE) to the access device. This step is performed only when CHAP authentication is used between the Portal server and access device. If PAP authentication is used, steps 7 and 8 are not performed.
- (Optional) The access device sends a Portal challenge response packet (ACK_CHALLENGE) to the Portal server.
- The Portal server encapsulates the entered user name and password into a Portal authentication request packet (REQ_AUTH) and sends the packet to the access device.
- The access device encapsulates the entered user name and password into a RADIUS authentication request packet (ACCESS-REQUEST) and sends the packet to the RADIUS server.
The RADIUS server authenticates the user name and password. If authentication succeeds, the RADIUS server sends an authentication accept packet (ACCESS-ACCEPT) to the access device. If authentication fails, the RADIUS server sends an authentication reject packet (ACCESS-REJECT) to the access device.
The ACCESS-ACCEPT packet also contains user authorization information because RADIUS authorization is combined with authentication and cannot be separated.
- The access device permits or denies the user access according to the authentication result. If the user access is permitted, the access device sends an accounting start request packet (ACCOUNTING-REQUEST) to the RADIUS server.
- The RADIUS server replies with an accounting start response packet (ACCOUNTING-RESPONSE), starts accounting, and adds the user to the local online user list.
- The access device sends the Portal authentication result (ACK_AUTH) to the Portal server and adds the user to the local online user list.
- The Portal server sends the Portal authentication result to the client to inform the client of successful authentication and adds the user to the local online user list.
- The Portal server sends an authentication acknowledgment packet (AFF_ACK_AUTH) to the access device.